C. elegans mitotic cyclins have distinct as well as overlapping functions in chromosome segregation
- PMID: 19829076
- PMCID: PMC3614003
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.24.10171
C. elegans mitotic cyclins have distinct as well as overlapping functions in chromosome segregation
Abstract
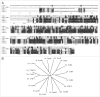
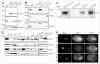
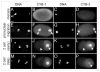
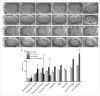
Mitotic cyclins in association with the Cdk1 protein kinase regulate progression through mitosis in all eukaryotes. Here, we address to what extent mitotic cyclins in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans provide overlapping functions or distinct biological activities. C. elegans expresses a single A-type cyclin (CYA-1), three typical B-type cyclins (CYB-1, CYB-2.1 and CYB-2.2), and one B3-subfamily member (CYB-3). While we observed clear redundancies between the cyb genes, cyb-1 and cyb-3 also contribute specific essential functions in meiosis and mitosis. CYB-1 and CYB-3 show similar temporal and spatial expression, both cyclins localize prominently to the nucleus, and both associate with CDK-1 and display histone H1 kinase activity in vitro. We demonstrate that inhibition of cyb-1 by RNAi interferes with chromosome congression and causes aneuploidy. In contrast, cyb-3(RNAi) embryos fail to initiate sister chromatid separation. Inhibition of both cyclins simultaneously results in a much earlier and more dramatic arrest. However, only the combination of cyb-1, cyb-3 and cyb-2.1/cyb-2.2 RNAi fully resembles cdk-1 inhibition. This combination of redundant and specific phenotypes supports that in vivo phosphorylation of certain Cdk targets can be achieved by multiple Cdk1/cyclin complexes, while phosphorylation of other targets requires a unique Cdk1/cyclin combination.
Figures
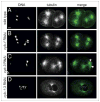
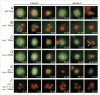
Comment in
-
The specific roles of mitotic cyclins revealed.Cell Cycle. 2010 Jan 1;9(1):22-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.1.10577. Epub 2010 Jan 1. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20016257 No abstract available.
References
-
- Morgan DO. Cyclin-dependent kinases: engines, clocks and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:261–91. - PubMed
-
- Satyanarayana A, Kaldis P. Mammalian cell cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene. 2009;28:2925–39. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274:1672–7. - PubMed
-
- Richardson H, Lew DJ, Henze M, Sugimoto K, Reed SI. Cyclin-B homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function in S phase and in G2. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2021–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
