Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 19830005
- PMCID: PMC2740325
- DOI: 10.4076/1757-1626-2-7735
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
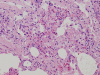
A 66-year-old female patient was admitted with a one year history of low-grade fever and shortness of breath with worsening symptoms. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest was performed, which revealed bilateral homogenous consolidation with subpleural predominance in the corresponding area. The percentage of eosinophils in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid was 98% and histological examination showed remarkable accumulation of eosinophils and lymphocytes in the alveoli and interstitium, with mild interstitial fibrosis. The diagnosis of idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia was confirmed. Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy (500 mg daily) for three days followed by 30 mg of oral prednisolone showed dramatic response. She was essentially normal after one year follow up.CEP is characterized by chronic and progressive clinical features and specific pathological findings. We review the epidemiology, clinical, diagnosis, and therapy of the CEP.
Figures
References
-
- Carrington CB, Addington WW, Goff AM, Madoff IM, Marks A, Schwaber JR, Gaensler EA. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. N Eng J Med. 1969;280:787–798. - PubMed
-
- Peter JJ, Sicilian L, Gaensler EA. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A report of 19 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine. 1988;67:154–162. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources