Brown tumor of the maxillary sinus in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism: a case report
- PMID: 19830212
- PMCID: PMC2737776
- DOI: 10.4076/1752-1947-3-7495
Brown tumor of the maxillary sinus in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Brown tumors are rare focal giant-cell lesions that arise as a direct result of the effect of parathyroid hormone on bone tissue in some patients with hyperparathyroidism. Brown tumors can affect the mandible, maxilla, clavicle, ribs, and pelvic bones. Therefore, diagnosis requires a systemic investigation for lesion differentiation.
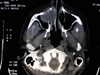
Case presentation: We present a 42-year-old Greek woman, with a rare case of brown tumor of the maxillary sinus due to primary hyperparathyroidism. Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by a solitary adenoma in 80% of cases and by glandular hyperplasia in 20%.
Conclusions: Differential diagnosis is important for the right treatment choice. It should exclude other giant cell lesions that affect the maxillae.
Figures


References
-
- Fitzgerald P. In: Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. 39. Tierney LMMcPhee SJPapadakis MA, editor. Appleton & Lange; 2000. pp. 1118–1121.
-
- Rosenberg EH, Guralnick WC. Hyperparathyroidism: A review of 220 proved cases, with special emphasis on findings in the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1962;15:84–94.
-
- Mirra JM. Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Correlations. Lea & Febiger; 1989. p. 1785.
-
- Som PM, Lawson W, Cohen BA. Giant cell lesions of the facial bones. Radiology. 1983;147:129–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

