Generation and analysis of a mouse line harboring GFP in the Eomes/Tbr2 locus
- PMID: 19830823
- PMCID: PMC7116378
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.20562
Generation and analysis of a mouse line harboring GFP in the Eomes/Tbr2 locus
Abstract
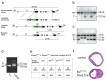
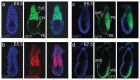
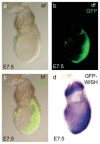
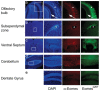
During mouse embryonic development, the T-box transcription factor Eomes/Tbr2 is expressed in highly dynamic patterns in various progenitor cell types. Those include the undifferentiated cells of the trophectoderm, ingressing nascent mesoderm at the primitive streak, and intermediate progenitor cells of the developing cerebral cortex. We generated an Eomes(GFP)- targeted allele to follow the highly dynamic patterns of Eomes expression and to allow for the identification of novel expression domains. We show that our novel allele recapitulates endogenous gene expression at known sites of expression and confirm our results by anti-Eomes immunofluorescent staining. Using this novel allele we were able to identify previously undocumented domains of Eomes expression within the visceral endoderm and at various locations in the developing and adult mouse brain.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Arnold SJ, Robertson EJ. Making a commitment: Cell lineage allocation and axis patterning in the early mouse embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Bulfone A, Martinez S, Marigo V, Campanella M, Basile A, Quaderi N, Gattuso C, Rubenstein JL, Ballabio A. Expression pattern of the Tbr2 (Eomesodermin) gene during mouse and chick brain development. Mech Dev. 1999;84:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Chazaud C, Rossant J. Disruption of early proximodistal patterning and AVE formation in Apc mutants. Development. 2006;133:3379–3387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

