Cross-regulation of signaling pathways by interferon-gamma: implications for immune responses and autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 19833085
- PMCID: PMC2774226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.09.002
Cross-regulation of signaling pathways by interferon-gamma: implications for immune responses and autoimmune diseases
Abstract
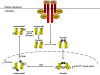
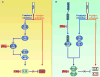
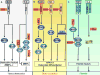
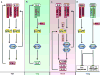
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is an important mediator of immunity and inflammation that utilizes the JAK-STAT signaling pathway to activate the STAT1 transcription factor. Many functions of IFN-gamma have been ascribed to direct STAT1-mediated induction of immune effector genes, but recently it has become clear that key IFN-gamma functions are mediated by cross-regulation of cellular responses to other cytokines and inflammatory factors. Here, we review mechanisms by which IFN-gamma and STAT1 regulate signaling by Toll-like receptors, inflammatory factors, tissue-destructive cytokines, anti-inflammatory cytokines, and cytokines that activate opposing STATs. These signaling mechanisms reveal insights about how IFN-gamma regulates macrophage activation, inflammation, tissue remodeling, and helper and regulatory T cell differentiation and how Th1 and Th17 cell responses are integrated in autoimmune diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Baccala R, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN. Interferons as pathogenic effectors in autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2005;204:9–26. - PubMed
-
- Baccarini M, Dello Sbarba P, Buscher D, Bartocci A, Stanley ER. IFN-gamma/lipopolysaccharide activation of macrophages is associated with protein kinase C-dependent down-modulation of the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor. J Immunol. 1992;149:2656–2661. - PubMed
-
- Barnes MJ, Powrie F. Hybrid Treg cells: steel frames and plastic exteriors. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:563–564. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Chadee K. Novel regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 production by IFN-gamma in human macrophages. J Immunol. 1998;161:2441–2448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

