Marked induction of the helix-loop-helix protein Id3 promotes the gammadelta T cell fate and renders their functional maturation Notch independent
- PMID: 19833086
- PMCID: PMC2768560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.07.010
Marked induction of the helix-loop-helix protein Id3 promotes the gammadelta T cell fate and renders their functional maturation Notch independent
Abstract
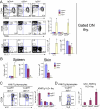
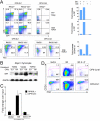
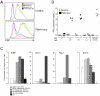
alphabeta and gammadelta T cells arise from a common thymocyte progenitor during development in the thymus. Emerging evidence suggests that the pre-T cell receptor (pre-TCR) and gammadelta T cell receptor (gammadeltaTCR) play instructional roles in specifying the alphabeta and gammadelta T-lineage fates, respectively. Nevertheless, the signaling pathways differentially engaged to specify fate and promote the development of these lineages remain poorly understood. Here, we show that differential activation of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)-early growth response gene (Egr)-inhibitor of DNA binding 3 (Id3) pathway plays a defining role in this process. In particular, Id3 expression served to regulate adoption of the gammadelta fate. Moreover, Id3 was both necessary and sufficient to enable gammadelta-lineage cells to differentiate independently of Notch signaling and become competent IFNgamma-producing effectors. Taken together, these findings identify Id3 as a central player that controls both adoption of the gammadelta fate and its maturation in the thymus.
Figures
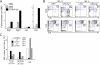



References
-
- Agata Y, Tamaki N, Sakamoto S, Ikawa T, Masuda K, Kawamoto H, Murre C. Regulation of T cell receptor beta gene rearrangements and allelic exclusion by the helix-loop-helix protein, E47. Immunity. 2007;27:871–884. - PubMed
-
- Carleton M, Haks MC, Smeele SA, Jones A, Belkowski SM, Berger MA, Linsley P, Kruisbeek AM, Wiest DL. Early growth response transcription factors are required for development of CD4(-)CD8(-) thymocytes to the CD4(+)CD8(+) stage. Journal of Immunology. 2002;168:1649–1658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

