HARPing on about the DNA damage response during replication
- PMID: 19833762
- PMCID: PMC2764495
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1860609
HARPing on about the DNA damage response during replication
Abstract
In this issue of Genes & Development, four papers report that the annealing helicase HepA-related protein (HARP, also known as SMARCAL1 [SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a-like 1]) binds directly to the ssDNA-binding protein Replication protein A (RPA) and is recruited to sites of replicative stress. Knockdown of HARP results in hypersensitivity to multiple DNA-damaging agents and defects in fork stability or restart. These exciting insights reveal a key new player in the S-phase DNA damage response.
Figures
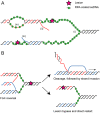
Comment on
-
The annealing helicase SMARCAL1 maintains genome integrity at stalled replication forks.Genes Dev. 2009 Oct 15;23(20):2405-14. doi: 10.1101/gad.1839909. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19793861 Free PMC article.
-
The SIOD disorder protein SMARCAL1 is an RPA-interacting protein involved in replication fork restart.Genes Dev. 2009 Oct 15;23(20):2415-25. doi: 10.1101/gad.1832309. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19793862 Free PMC article.
-
The annealing helicase HARP is recruited to DNA repair sites via an interaction with RPA.Genes Dev. 2009 Oct 15;23(20):2400-4. doi: 10.1101/gad.1831509. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19793863 Free PMC article.
-
The annealing helicase HARP protects stalled replication forks.Genes Dev. 2009 Oct 15;23(20):2394-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1836409. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19793864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbour L, Xiao W. Regulation of alternative replication bypass pathways at stalled replication forks and its effects on genome stability: A yeast model. Mutat Res. 2003;532:137–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
