Impact of an organizational intervention designed to improve snack and beverage quality in YMCA after-school programs
- PMID: 19833987
- PMCID: PMC2853616
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.158907
Impact of an organizational intervention designed to improve snack and beverage quality in YMCA after-school programs
Abstract
Objectives: We evaluated the quality of snacks and beverages served at YMCA after-school programs before and after the programs' participation in a YMCA Learning Collaborative.
Methods: We collected data on the types and brands of snacks and beverages (including fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, foods with trans fats, water, and sugar-sweetened beverages) served daily during 3 different time periods spanning 14 months in total, and the components of the healthy eating standards. We compared snack and beverage quality before and after the intervention.
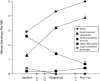
Results: Weekly servings of fresh fruits and vegetables (1.3 vs 3.9; P = .02) and weekly servings of fruits and vegetables as a whole (1.9 vs 5.2; P = .009) increased from baseline to postintervention; weekly servings of desserts (1.3 vs 0.5; P = .049), foods with added sugars (3.9 vs 2.4; P = .03), and foods containing trans fats (2.6 vs 0.7; P = .01) decreased. After the intervention, all YMCAs offered water daily, and none served sugar-sweetened beverages. The percentage of calories from fruits and vegetables significantly increased after the intervention, whereas the percentage of calories from foods containing trans fats and added sugars decreased.
Conclusions: A learning collaborative can disseminate healthy eating standards among participating organizations and facilitate improvements in the quality of after-school snacks and beverages.
Figures
References
-
- Afterschool Alliance America After 3 PM: executive summary. Available at: http://www.afterschoolalliance.org/documents/AA%203%20pm_Executive_Summa.... Accessed August 29, 2009
-
- Carver PR, Iruka IU, Chapman C. National Household Education Surveys Program of 2005: After-School Programs and Activities Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics; 2006
-
- Health 2006, With Chartbook on Trends in the Health of Americans Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2006 - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. High body mass index for age among US children and adolescents, 2003–2006. JAMA 2008;299:2401–2405 - PubMed
-
- Wang YC, Gortmaker SL, Sobol AM, Kuntz KM. Estimating the energy gap among US children: a counterfactual approach. Pediatrics 2006;118:e1721–e1733 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources