Presenilins are enriched in endoplasmic reticulum membranes associated with mitochondria
- PMID: 19834068
- PMCID: PMC2774047
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090219
Presenilins are enriched in endoplasmic reticulum membranes associated with mitochondria
Abstract
Presenilin-1 (PS1) and -2 (PS2), which when mutated cause familial Alzheimer disease, have been localized to numerous compartments of the cell, including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi, nuclear envelope, endosomes, lysosomes, the plasma membrane, and mitochondria. Using three complementary approaches, subcellular fractionation, gamma-secretase activity assays, and immunocytochemistry, we show that presenilins are highly enriched in a subcompartment of the endoplasmic reticulum that is associated with mitochondria and that forms a physical bridge between the two organelles, called endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria-associated membranes. A localization of PS1 and PS2 in mitochondria-associated membranes may help reconcile the disparate hypotheses regarding the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease and may explain many seemingly unrelated features of this devastating neurodegenerative disorder.
Figures
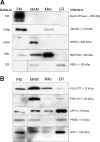
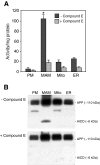

References
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG. A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2006;314:777–781. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi T, De Strooper B. Presenilins: members of the γ-secretase quartets, but part-time soloists too. Physiology. 2008;23:194–204. - PubMed
-
- De Strooper B, Beullens M, Contreras B, Levesque L, Craessaerts K, Cordell B, Moechars D, Bollen M, Fraser P, George-Hyslop PS, Van Leuven F. Phosphorylation, subcellular localization, and membrane orientation of the Alzheimer’s disease-associated presenilins. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3590–3598. - PubMed
-
- Siman R, Velji J. Localization of presenilin-nicastrin complexes and γ-secretase activity to the trans-Golgi network. J Neurochem. 2003;84:1143–1153. - PubMed
-
- Chyung JH, Raper DM, Selkoe DJ. γ-Secretase exists on the plasma membrane as an intact complex that accepts substrates and effects intramembrane cleavage. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:4383–4392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS11766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM045735/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HD83062/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- GM61721/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM45735/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA13696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG05136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG08702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS011766/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG014930/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM66037/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061721/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

