Modifications of RNA polymerase II are pivotal in regulating gene expression states
- PMID: 19834511
- PMCID: PMC2775184
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.221
Modifications of RNA polymerase II are pivotal in regulating gene expression states
Abstract
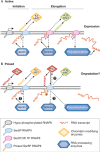
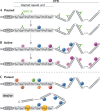
The regulation of gene expression programmes is essential for the generation of diverse cell types during development and for adaptation to environmental signals. RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcribes genetic information and coordinates the recruitment of accessory proteins that are responsible for the establishment of active chromatin states and transcript maturation. RNAPII is post-translationally modified at active genes during transcription initiation, elongation and termination, and thereby recruits specific histone and RNA modifiers. RNAPII complexes are also located at silent genes in promoter-proximal paused configurations that provide dynamic transcriptional regulation downstream from initiation. In embryonic stem cells, silent developmental regulator genes that are repressed by Polycomb are associated with a form of RNAPII that can elongate through coding regions but that lacks the post-translational modifications that are important for coupling RNA synthesis to co-transcriptional maturation. Here, we discuss the mechanisms through which the transcription of silent genes might be dissociated from productive expression, and the sophisticated interplay between the transcriptional machinery, Polycomb repression and RNA processing.
Figures
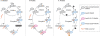
References
-
- Azuara V et al. (2006) Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat Cell Biol 8: 532–538 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE et al. (2006) A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 125: 315–326 - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA et al. (2006) Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature 441: 349–353 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

