Induction of membrane ceramides: a novel strategy to interfere with T lymphocyte cytoskeletal reorganisation in viral immunosuppression
- PMID: 19834551
- PMCID: PMC2757718
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000623
Induction of membrane ceramides: a novel strategy to interfere with T lymphocyte cytoskeletal reorganisation in viral immunosuppression
Abstract
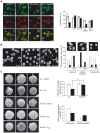
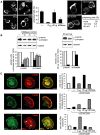
Silencing of T cell activation and function is a highly efficient strategy of immunosuppression induced by pathogens. By promoting formation of membrane microdomains essential for clustering of receptors and signalling platforms in the plasma membrane, ceramides accumulating as a result of membrane sphingomyelin breakdown are not only essential for assembly of signalling complexes and pathogen entry, but also act as signalling modulators, e. g. by regulating relay of phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signalling. Their role in T lymphocyte functions has not been addressed as yet. We now show that measles virus (MV), which interacts with the surface of T cells and thereby efficiently interferes with stimulated dynamic reorganisation of their actin cytoskeleton, causes ceramide accumulation in human T cells in a neutral (NSM) and acid (ASM) sphingomyelinase-dependent manner. Ceramides induced by MV, but also bacterial sphingomyelinase, efficiently interfered with formation of membrane protrusions and T cell spreading and front/rear polarisation in response to beta1 integrin ligation or alphaCD3/CD28 activation, and this was rescued upon pharmacological or genetic ablation of ASM/NSM activity. Moreover, membrane ceramide accumulation downmodulated chemokine-induced T cell motility on fibronectin. Altogether, these findings highlight an as yet unrecognised concept of pathogens able to cause membrane ceramide accumulation to target essential processes in T cell activation and function by preventing stimulated actin cytoskeletal dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

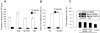
References
-
- Bollinger CR, Teichgraber V, Gulbins E. Ceramide-enriched membrane domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1746:284–294. - PubMed
-
- Grassme H, Jekle A, Riehle A, Schwarz H, Berger J, et al. CD95 signalling via ceramide-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20589–20596. - PubMed
-
- Church LD, Hessler G, Goodall JE, Rider DA, Workman CJ, et al. TNFR1-induced sphingomyelinase activation modulates TCR signalling by impairing store-operated Ca2+ influx. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:266–278. - PubMed
-
- Gulbins E, Grassme H. Ceramide and cell death receptor clustering. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1585:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Abdel Shakor AB, Kwiatkowska K, Sobota A. Cell surface ceramide generation precedes and controls FcgammaRII clustering and phosphorylation in rafts. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:36778–36787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

