Structure and signaling mechanism of Per-ARNT-Sim domains
- PMID: 19836329
- PMCID: PMC3092527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2009.08.011
Structure and signaling mechanism of Per-ARNT-Sim domains
Abstract
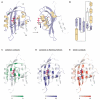
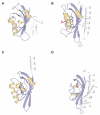
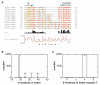
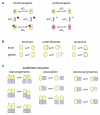
Per-ARNT-Sim (PAS) domains serve as versatile sensor and interaction modules in signal transduction proteins. PAS sensors detect chemical and physical stimuli and regulate the activity of functionally diverse effector domains. In contrast to this chemical, physical, and functional diversity, the structure of the core of PAS domains is broadly conserved and comprises a five-stranded antiparallel beta sheet and several alpha helices. Signals originate within the conserved core and generate structural and dynamic changes predominantly within the beta sheet, from which they propagate via amphipathic alpha-helical and coiled-coil linkers at the N or C termini of the core to the covalently attached effector domain. Effector domains are typically dimeric; their activity appears to be largely regulated by signal-dependent changes in quaternary structure and dynamics. The signaling mechanisms of PAS and other signaling domains share common features, and these commonalities can be exploited to enable structure-based design of artificial photosensors and chemosensors.
Figures


References
-
- Anantharaman V, Aravind L. Cache - a signaling domain common to animal Ca(2+)-channel subunits and a class of prokaryotic chemotaxis receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:535–537. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman V, Koonin EV, Aravind L. Regulatory potential, phyletic distribution and evolution of ancient, intracellular small-molecule-binding domains. J Mol Biol. 2001;307:1271–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

