Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs
- PMID: 19836392
- PMCID: PMC4758813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.024
Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs
Abstract
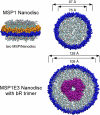
Nanodiscs are soluble nanoscale phospholipid bilayers which can self-assemble integral membrane proteins for biophysical, enzymatic or structural investigations. This means for rendering membrane proteins soluble at the single molecule level offers advantages over liposomes or detergent micelles in terms of size, stability, ability to add genetically modifiable features to the Nanodisc structure and ready access to both sides of the phospholipid bilayer domain. Thus the Nanodisc system provides a novel platform for understanding membrane protein function. We provide an overview of the Nanodisc approach and document through several examples many of the applications to the study of the structure and function of integral membrane proteins.
Copyright 2009 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bayburt TH, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG. Nano Lett. 2002;2:853–856.
-
- Shih AY, Freddolino PL, Sligar SG, Schulten K. Nano Lett. 2007;7:1692–1696. - PubMed
-
- Shih AY, Freddolino PL, Arkhipov A, Schulten K. J. Struct. Biol. 2007;157:579–592. - PubMed
-
- Denisov IG, Grinkova YV, Lazarides AA, Sligar SG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:3477–3487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

