Partial versus radical nephrectomy for 4 to 7 cm renal cortical tumors
- PMID: 19836797
- PMCID: PMC4171846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.087
Partial versus radical nephrectomy for 4 to 7 cm renal cortical tumors
Abstract
Purpose: Recent observations suggest that partial nephrectomy for small renal tumors may be associated with improved survival compared with radical nephrectomy. We evaluated survival in patients with 4 to 7 cm renal tumors in a bi-institutional collaboration.
Materials and methods: By combining institutional databases from Mayo Clinic and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center we identified 1,159 patients with 4.1 to 7.0 cm sporadic, unilateral, solitary, localized renal masses who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy between 1989 and 2006. Patient outcome was compared using Cox proportional hazards regression models.
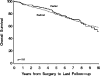
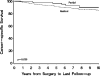
Results: Of the 1,159 patients 873 (75%) and 286 (25%) were treated with radical and partial nephrectomy, respectively. Patients treated with partial vs radical nephrectomy were significantly more likely to have a solitary kidney (10% vs 0.2%) and chronic kidney disease (15% vs 7%, each p <0.001). Median followup in survivors was 4.8 years (range 0 to 19). There was no significant difference in overall survival in patients treated with radical vs partial nephrectomy (p = 0.8). Of 943 patients with renal cell carcinoma those treated with radical nephrectomy were significantly more likely to die of renal cell carcinoma than those treated with partial nephrectomy (HR 2.16, 95% CI 1.04-4.50, p = 0.039) but this only approached statistical significance on multivariate analysis (HR 1.97, 95% CI 0.92-4.20, p = 0.079).
Conclusions: Results suggest that overall and cancer specific survival is not compromised when partial nephrectomy is done for 4 to 7 cm renal cortical tumors. With the benefit of preserving renal function our results support partial nephrectomy when technically feasible for renal tumors up to 7 cm.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial comment.J Urol. 2009 Dec;182(6):2606. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.197. Epub 2009 Oct 17. J Urol. 2009. PMID: 19836796 No abstract available.
References
-
- Patard JJ, Shvarts O, Lam JS, Pantuck AJ, Kim HL, Ficarra V, et al. Safety and efficacy of partial nephrectomy for all T1 tumors based on an international multicenter experience. J Urol. 2004;171:2181. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RH, Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Blute ML. Complications of contemporary open nephron sparing surgery: a single institution experience. J Urol. 2005;174:855. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED, Cheville JC, et al. Radical nephrectomy for pT1a renal masses may be associated with decreased overall survival compared with partial nephrectomy. J Urol. 2008;179:468. - PubMed
-
- Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL, Zincke H. Nephron sparing surgery for appropriately selected renal cell carcinoma between 4 and 7 cm results in outcome similar to radical nephrectomy. J Urol. 2004;171:1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

