Notch-1 activates estrogen receptor-alpha-dependent transcription via IKKalpha in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 19838210
- PMCID: PMC4976641
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.323
Notch-1 activates estrogen receptor-alpha-dependent transcription via IKKalpha in breast cancer cells
Abstract
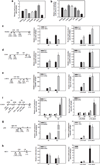
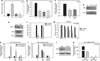
Approximately 80% of breast cancers express the estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and are treated with anti-estrogens. Resistance to these agents is a major cause of mortality. We have shown that estrogen inhibits Notch, whereas anti-estrogens or estrogen withdrawal activate Notch signaling. Combined inhibition of Notch and estrogen signaling has synergistic effects in ERalpha-positive breast cancer models. However, the mechanisms whereby Notch-1 promotes the growth of ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells are unknown. Here, we demonstrate that Notch-1 increases the transcription of ERalpha-responsive genes in the presence or absence of estrogen via a novel chromatin crosstalk mechanism. Our data support a model in which Notch-1 can activate the transcription of ERalpha-target genes via IKKalpha-dependent cooperative chromatin recruitment of Notch-CSL-MAML1 transcriptional complexes (NTC) and ERalpha, which promotes the recruitment of p300. CSL binding elements frequently occur in close proximity to estrogen-responsive elements (EREs) in the human and mouse genomes. Our observations suggest that a hitherto unknown Notch-1/ERalpha chromatin crosstalk mediates Notch signaling effects in ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells and contributes to regulate the transcriptional functions of ERalpha itself.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
p53 Modulates Notch Signaling in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Associating With the Notch Transcriptional Complex Via MAML1.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec;230(12):3115-27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25052. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26033683 Free PMC article.
-
An H3K4me3 reader, BAP18 as an adaptor of COMPASS-like core subunits co-activates ERα action and associates with the sensitivity of antiestrogen in breast cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):10768-10784. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa787. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32986841 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 is a transcriptional target of ERalpha and has a critical role in breast cancer endocrine sensitivity and resistance.Oncogene. 2010 May 20;29(20):2983-95. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.47. Epub 2010 Mar 8. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20208560 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of estrogen receptor-α upregulation in breast cancers.Med Mol Morphol. 2010 Dec;43(4):193-6. doi: 10.1007/s00795-010-0514-3. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Med Mol Morphol. 2010. PMID: 21267694 Review.
-
The complex relationship between BRCA1 and ERalpha in hereditary breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;15(5):1514-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0640. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19223511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Notch activation stimulates migration of breast cancer cells and promotes tumor growth.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R54. doi: 10.1186/bcr3447. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23826634 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between PKCα and Notch-4 in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells.Oncogenesis. 2013 Aug 5;2(8):e60. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2013.26. Oncogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23917222 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1 mediates uterine stromal differentiation and is critical for complete decidualization in the mouse.FASEB J. 2012 Jan;26(1):282-94. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-184663. Epub 2011 Oct 11. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 21990372 Free PMC article.
-
Benzothiophenone Derivatives Targeting Mutant Forms of Estrogen Receptor-α in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 15;19(2):579. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020579. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29462880 Free PMC article.
-
17β-estradiol enhances signalling mediated by VEGF-A-delta-like ligand 4-notch1 axis in human endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e71440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071440. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arsura M, Panta GR, Bilyeu JD, Cavin LG, Sovak MA, Oliver AA, et al. Transient activation of NF-kappaB through a TAK1/ IKK kinase pathway by TGF-beta1 inhibits AP-1/SMAD signaling and apoptosis: implications in liver tumor formation. Oncogene. 2003;22:412–425. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Baonza A, Freeman M. Control of cell proliferation in the Drosophila eye by Notch signaling. Dev Cell. 2005;8:529–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

