CaMKII associates with CaV1.2 L-type calcium channels via selected beta subunits to enhance regulatory phosphorylation
- PMID: 19840220
- PMCID: PMC2814318
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06436.x
CaMKII associates with CaV1.2 L-type calcium channels via selected beta subunits to enhance regulatory phosphorylation
Abstract
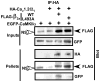
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) facilitates L-type calcium channel (LTCC) activity physiologically, but may exacerbate LTCC-dependent pathophysiology. We previously showed that CaMKII forms stable complexes with voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC) beta(1b) or beta(2a) subunits, but not with the beta(3) or beta(4) subunits (Grueter et al. 2008). CaMKII-dependent facilitation of Ca(V)1.2 LTCCs requires Thr498 phosphorylation in the beta(2a) subunit (Grueter et al. 2006), but the relationship of this modulation to CaMKII interactions with LTCC subunits is unknown. Here we show that CaMKII co-immunoprecipitates with forebrain LTCCs that contain Ca(V)1.2alpha(1) and beta(1) or beta(2) subunits, but is not detected in LTCC complexes containing beta(4) subunits. CaMKIIalpha can be specifically tethered to the I/II linker of Ca(V)1.2 alpha(1) subunits in vitro by the beta(1b) or beta(2a) subunits. Efficient targeting of CaMKIIalpha to the full-length Ca(V)1.2alpha(1) subunit in transfected HEK293 cells requires CaMKII binding to the beta(2a) subunit. Moreover, disruption of CaMKII binding substantially reduced phosphorylation of beta(2a) at Thr498 within the LTCC complex, without altering overall phosphorylation of Ca(V)1.2alpha(1) and beta subunits. These findings demonstrate a biochemical mechanism underlying LTCC facilitation by CaMKII.
Figures
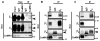



References
-
- Anderson ME, Braun AP, Schulman H, Premack BA. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates Ca(2+)-induced enhancement of the L-type Ca2+ current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 1994;75:854–861. - PubMed
-
- Berggren PO, Yang SN, Murakami M, et al. Removal of Ca2+ channel beta3 subunit enhances Ca2+ oscillation frequency and insulin exocytosis. Cell. 2004;119:273–284. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:23–49. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L, Qin N, Olcese R, Tareilus E, Platano D, Costantin J, Stefani E. Structures and functions of calcium channel beta subunits. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1998;30:357–375. - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt J, Helmstadter K, Wu X, Clements-Jewery H, Haworth RS, Avkiran M, Martin JL, Pogwizd SM, Bers DM. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIdelta and protein kinase D overexpression reinforce the histone deacetylase 5 redistribution in heart failure. Circ Res. 2008;102:695–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

