Increased intranuclear matrix metalloproteinase activity in neurons interferes with oxidative DNA repair in focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 19840223
- PMCID: PMC4950937
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06433.x
Increased intranuclear matrix metalloproteinase activity in neurons interferes with oxidative DNA repair in focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
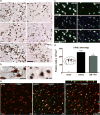
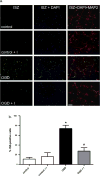
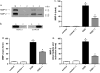
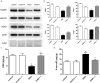
Increased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity is implicated in proteolysis of extracellular matrix in ischemic stroke. We recently observed intranuclear MMP activity in ischemic brain neurons at early reperfusion, suggesting a possible role in nuclear matrix proteolysis. Nuclear proteins, poly-ADP-ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1) and X-ray cross-complementary factor 1 (XRCC1), as well as DNA repair enzymes, are important in DNA fragmentation and cell apoptosis. We hypothesized that intranuclear MMP activity facilitates oxidative injury in neurons during early ischemic insult by cleaving PARP-1 and XRCC1, interfering with DNA repair. We induced a 90-min middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Increase activity of MMP-2 and -9, detected in the ischemic neuronal nuclei at 3 h, was associated with DNA fragmentation at 24 and 48 h reperfusion. The intranuclear MMPs cleaved PARP-1. Treatment of the rats with a broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor, BB1101, significantly attenuated ischemia-induced PARP-1 cleavage, increasing its activity. Degradation of XRCC1 caused by ischemic insult in rat brain was also significantly attenuated by BB1101. We found elevation of oxidized DNA, apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine, in ischemic brain cells at 3 h reperfusion. BB1101 markedly attenuated the early increase of oxidized DNA. Using tissue from stroke patients, we found increased intranuclear MMP expression. Our data suggest that intranuclear MMP activity cleaves PARP-1 and XRCC1, interfering with oxidative DNA repair. This novel role for MMPs could contribute to neuronal apoptosis in ischemic injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ali MA, Schulz R. Activation of MMP-2 as a key event in oxidative stress injury to the heart. Front Biosci. 2009;14:699–716. - PubMed
-
- Amantea D, Corasaniti MT, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G, Bagetta G. Brain regional and cellular localization of gelatinase activity in rat that have undergone transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroscience. 2008;152:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Amantea D, Russo R, Gliozzi M, Fratto V, Berliocchi L, Bagetta G, Bernardi G, Corasaniti MT. Early upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases following reperfusion triggers neuroinflammatory mediators in brain ischemia in rat. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;82:149–169. - PubMed
-
- Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ, Fini ME, Lo EH. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1681–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

