miR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: IMPLICATION IN INNATE IMMUNITY
- PMID: 19840932
- PMCID: PMC2787321
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056317
miR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: IMPLICATION IN INNATE IMMUNITY
Abstract
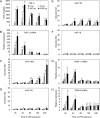
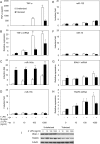
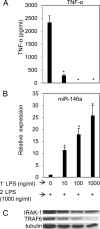
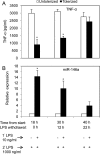
The human toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway is activated in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and subsequent signal transductions lead to the production of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) by innate immune cells. Defects in innate immune response may contribute to the overproduction of TNF-alpha leading to systemic inflammation and diseases. Thus, the innate immune response needs to be tightly regulated by elaborate mechanisms to control its onset and termination. LPS tolerance is a state of hyporesponsiveness to subsequent LPS challenge and is achieved by monocytic cells after prolonged exposure to LPS. In this report, kinetics of endotoxin-responsive microRNAs expression analysis revealed a unique pattern of gradual increase for miR-146a starting 4 h after LPS stimulation in THP-1 cells and continued up to 35-fold over 24 h. Conversely, TNF-alpha increased up to 4 h and then decreased gradually implicating a negative correlation with miR-146a progression. The characteristic up-regulation of miR-146a toward subsequent LPS challenge in THP-1 cells was studied. Strikingly, microRNA expression analysis during the tolerized state of THP-1 cells showed only miR-146a overexpression suggesting its important role in LPS tolerance. In addition, LPS tolerance was dependent on a LPS-priming dose and associated miR-146a up-regulation. LPS-tolerized cells were observed to regain responsiveness in TNF-alpha production 22 h after LPS removal correlating with a decrease in miR-146a level. Transfection of miR-146a into THP-1 cells mimicked LPS priming, whereas transfection of miR-146a inhibitor largely abolished LPS tolerance. Thus our studies demonstrated that miR-146a is critical for the in vitro monocytic cell-based endotoxin tolerance.
Figures
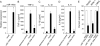
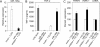

Similar articles
-
Mechanistic role of microRNA-146a in endotoxin-induced differential cross-regulation of TLR signaling.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 1;186(3):1723-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002311. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21178010 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 1β-Responsive MicroRNA-146a Is Critical for the Cytokine-Induced Tolerance and Cross-Tolerance to Toll-Like Receptor Ligands.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(4):428-40. doi: 10.1159/000371517. Epub 2015 Apr 18. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25896300 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-146a induction by cyanobacterial lipopolysaccharide antagonist (CyP) mediates endotoxin cross-tolerance.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 27;8(1):11367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29820-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30054544 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance.Cell Mol Immunol. 2011 Sep;8(5):388-403. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.26. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21822296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of miR-146a: Targeting innate inflammation in atherosclerosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(19):e70121. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70121. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39392102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of innate immunity in neonatal infection.Am J Perinatol. 2013 Feb;30(2):105-12. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1333412. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Am J Perinatol. 2013. PMID: 23297181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphine induced exacerbation of sepsis is mediated by tempering endotoxin tolerance through modulation of miR-146a.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1977. doi: 10.1038/srep01977. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23756365 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA and its network in the pathogenesis of Myasthenia Gravis.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Sep 10;11:1388476. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1388476. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39318549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absence of miRNA-146a Differentially Alters Microglia Function and Proteome.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 5;11:1110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01110. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582192 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of gene and microRNA expression profiles reveals candidate biomarkers and regulatory networks in psoriasis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e39002. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039002. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39028999 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

