Site-specific phosphorylation induces functionally active conformation in the intrinsically disordered N-terminal activation function (AF1) domain of the glucocorticoid receptor
- PMID: 19841061
- PMCID: PMC2798295
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00552-09
Site-specific phosphorylation induces functionally active conformation in the intrinsically disordered N-terminal activation function (AF1) domain of the glucocorticoid receptor
Abstract
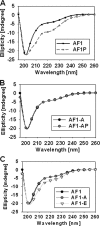
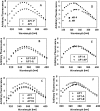
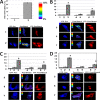
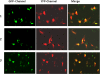
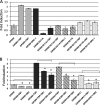
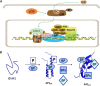
Intrinsically disordered (ID) regions are disproportionately higher in cell signaling proteins and are predicted to have much larger frequency of phosphorylation sites than ordered regions, suggesting an important role in their regulatory capacity. In this study, we show that AF1, an ID activation domain of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), adopts a functionally folded conformation due to its site-specific phosphorylation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, which is involved in apoptotic and gene-inductive events initiated by the GR. Further, we show that site-specific phosphorylation-induced secondary and tertiary structure formation specifically facilitates AF1's interaction with critical coregulatory proteins and subsequently its transcriptional activity. These data demonstrate a mechanism through which ID activation domain of the steroid receptors and other similar transcription factors may adopt a functionally active conformation under physiological conditions.
Figures




References
-
- Andrade, M.A., P. Chacón, J. J. Merelo, and F. Morán. 1993. Evaluation of secondary structure of proteins from UV circular dichroism using an unsupervised learning neural network. Protein Eng. 6:383-390. - PubMed
-
- Bai, Y., and V. Giguére. 2003. Isoform-selective interactions between estrogen receptors and steroid receptor coactivators promoted by estradiol and ErbB-2 signaling in living cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 17:589-599. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, R. L., and G. D. Rose. 1999. Is protein folding hierarchic? II. Folding intermediates and transition states. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:77-83. - PubMed
-
- Baskakov, I. V., R. Kumar, G. Srinivasan, Y. Ji, D. W. Bolen, and E. B. Thompson. 1999. Trimethylamine N-oxide-induced cooperative folding of an intrinsically unfolded transcription-activating fragment of human glucocorticoid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274:10693-10696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
