Functional cooperation of the proapoptotic Bcl2 family proteins Bmf and Bim in vivo
- PMID: 19841067
- PMCID: PMC2798311
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01155-09
Functional cooperation of the proapoptotic Bcl2 family proteins Bmf and Bim in vivo
Abstract
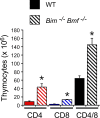
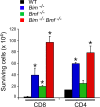
Bcl2-modifying factor (Bmf) is a member of the BH3-only group of proapoptotic proteins. To test the role of Bmf in vivo, we constructed mice with a series of mutated Bmf alleles that disrupt Bmf expression, prevent Bmf phosphorylation by the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) on Ser(74), or mimic Bmf phosphorylation on Ser(74). We report that the loss of Bmf causes defects in uterovaginal development, including an imperforate vagina and hydrometrocolpos. We also show that the phosphorylation of Bmf on Ser(74) can contribute to a moderate increase in levels of Bmf activity. Studies of compound mutants with the related gene Bim demonstrated that Bim and Bmf exhibit partially redundant functions in vivo. Thus, developmental ablation of interdigital webbing on mouse paws and normal lymphocyte homeostasis require the cooperative activity of Bim and Bmf.
Figures
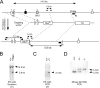
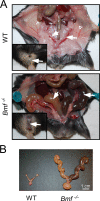
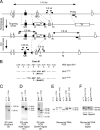


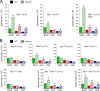
References
-
- Bouillet, P., D. Metcalf, D. C. Huang, D. M. Tarlinton, T. W. Kay, F. Kontgen, J. M. Adams, and A. Strasser. 1999. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286:1735-1738. - PubMed
-
- Cecconi, F., G. Alvarez-Bolado, B. I. Meyer, K. A. Roth, and P. Gruss. 1998. Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development. Cell 94:727-737. - PubMed
-
- Davis, R. J. 2000. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239-252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
