Prospective identification, isolation, and systemic transplantation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in murine bone marrow
- PMID: 19841085
- PMCID: PMC2768869
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091046
Prospective identification, isolation, and systemic transplantation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in murine bone marrow
Abstract
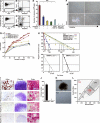
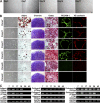
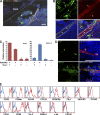
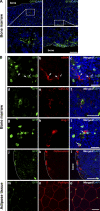
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are defined as cells that undergo sustained in vitro growth and can give rise to multiple mesenchymal lineages. Because MSCs have only been isolated from tissue in culture, the equivalent cells have not been identified in vivo and little is known about their physiological roles or even their exact tissue location. In this study, we used phenotypic, morphological, and functional criteria to identify and prospectively isolate a subset of MSCs (PDGFRalpha+Sca-1+CD45-TER119-) from adult mouse bone marrow. Individual MSCs generated colonies at a high frequency and could differentiate into hematopoietic niche cells, osteoblasts, and adipocytes after in vivo transplantation. Naive MSCs resided in the perivascular region in a quiescent state. This study provides the useful method needed to identify MSCs as defined in vivo entities.
Figures


References
-
- Bacon E.R., Sytkowski A.J. 1987. Identification and characterization of a differentiation-specific antigen on normal and malignant murine erythroid cells. Blood. 69:103–108 - PubMed
-
- Barbash I.M., Chouraqui P., Baron J., Feinberg M.S., Etzion S., Tessone A., Miller L., Guetta E., Zipori D., Kedes L.H., et al. 2003. Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution. Circulation. 108:863–868 10.1161/01.CIR.0000084828.50310.6A - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

