Nanoparticle-based bio-barcode assay redefines "undetectable" PSA and biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy
- PMID: 19841273
- PMCID: PMC2773980
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904719106
Nanoparticle-based bio-barcode assay redefines "undetectable" PSA and biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy
Abstract
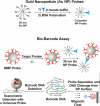
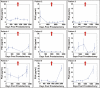
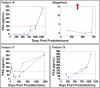
We report the development of a previously undescribed gold nanoparticle bio-barcode assay probe for the detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) at 330 fg/mL, automation of the assay, and the results of a clinical pilot study designed to assess the ability of the assay to detect PSA in the serum of 18 men who have undergone radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. Due to a lack of sensitivity, available PSA immunoassays are often not capable of detecting PSA in the serum of men after radical prostatectomy. This new bio-barcode PSA assay is approximately 300 times more sensitive than commercial immunoassays. Significantly, with the barcode assay, every patient in this cohort had a measurable serum PSA level after radical prostatectomy. Patients were separated into categories based on PSA levels as a function of time. One group of patients showed low levels of PSA with no significant increase with time and did not recur. Others showed, at some point postprostatectomy, rising PSA levels. The majority recurred. Therefore, this new ultrasensitive assay points to significant possible outcomes: (i) The ability to tell patients, who have undetectable PSA levels with conventional assays, but detectable and nonrising levels with the barcode assay, that their cancer will not recur. (ii) The ability to assign recurrence earlier because of the ability to measure increasing levels of PSA before conventional tools can make such assignments. (iii) The ability to use PSA levels that are not detectable with conventional assays to follow the response of patients to adjuvant or salvage therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.A.M., C.S.T., and N.D.S. are shareholders in Nanosphere, Inc., the company which licensed the bio-barcode assay from Northwestern University.
Figures


References
-
- Ries LAG, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2005. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2008.
-
- Oesterling JE, et al. The periurethral glands do not significantly influence the serum prostate specific antigen concentration. J Urol. 1996;155:1658–1660. - PubMed
-
- Bock JL, Klee GG. How sensitive is a prostate-specific antigen measurement? How sensitive does it need to be? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128:341–343. - PubMed
-
- Schroeder FH, et al. Screening and Prostate-Cancer Mortality in a Randomized European Study. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1320–1328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

