Epidemiologic study on survival of chronic myeloid leukemia and Ph(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients with BCR-ABL T315I mutation
- PMID: 19843886
- PMCID: PMC4916939
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-219410
Epidemiologic study on survival of chronic myeloid leukemia and Ph(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients with BCR-ABL T315I mutation
Abstract
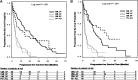
The BCR-ABL T315I mutation represents a major mechanism of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The objectives of this retrospective observational study were to estimate overall and progression-free survival for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic-phase (CP), accelerated-phase (AP), or blastic-phase (BP) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph)(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients with T315I mutation. Medical records of 222 patients from 9 countries were reviewed; data were analyzed using log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazard models. Median age at T315I mutation detection was 54 years; 57% cases were men. Median time between TKI treatment initiation and T315I mutation detection was 29.2, 15.4, 5.8, and 9.1 months, respectively, for CP, AP, BP, and Ph(+) ALL patients. After T315I mutation detection, second-generation TKIs were used in 56% of cases, hydroxyurea in 39%, imatinib in 35%, cytarabine in 26%, MK-0457 in 11%, stem cell transplantation in 17%, and interferon-alpha in 6% of cases. Median overall survival from T315I mutation detection was 22.4, 28.4, 4.0, and 4.9 months, and median progression-free survival was 11.5, 22.2, 1.8, and 2.5 months, respectively, for CP, AP, BP, and Ph(+) ALL patients. These results confirm that survival of patients harboring a T315I mutation is dependent on disease phase at the time of mutation detection.
Figures


References
-
- O'Hare T, Eide CA, Deininger MW. Bcr-Abl kinase domain mutations, drug resistance, and the road to a cure for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2007;110(7):2242–2249. - PubMed
-
- Soverini S, Colarossi S, Gnani A, et al. Contribution of ABL kinase domain mutations to imatinib resistance in different subsets of Philadelphia-positive patients: by the GIMEMA Working Party on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(24):7374–7379. - PubMed
-
- Soverini S, Iacobucci I, Baccarani M, Martinelli G. Targeted therapy and the T315I mutation in Philadelphia-positive leukemias. Haematologica. 2007;92(04):437–439. - PubMed
-
- Soverini S, Colarossi S, Gnani A, et al. Resistance to dasatinib in Philadelphia-positive leukemia patients and the presence or the selection of mutations at residues 315 and 317 in the BCR-ABL kinase domain. Haematologica. 2007;92(04):401–404. - PubMed
-
- Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, et al. Detection of BCR-ABL mutations in patients with CML treated with imatinib is virtually always accompanied by clinical resistance, and mutations in the ATP phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) are associated with a poor prognosis. Blood. 2003;102(1):276–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

