Comparison of 5 health-related quality-of-life indexes using item response theory analysis
- PMID: 19843961
- PMCID: PMC2812696
- DOI: 10.1177/0272989X09347016
Comparison of 5 health-related quality-of-life indexes using item response theory analysis
Abstract
Background: Five health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL) indexes--EQ-5D, HUI2, HUI3, QWB-SA, and SF-6D--are each used to assign community-based utility scores to health states, although these scores differ.
Objective: The authors transform these indexes to a common scale to understand their interrelationships.
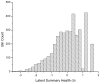
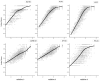
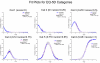
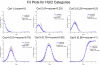
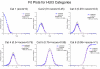
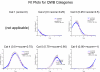
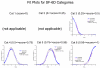
Methods: Data were from the National Health Measurement Study, a telephone survey of 3844 US adults. The 5 indexes were analyzed using item response theory analysis to estimate scores on an underlying construct of summary health, theta. Unidimensionality was evaluated using nonlinear principal components analysis. Index scores were plotted against the estimated scores on the common underlying construct. In addition, scores on the Health and Activities Limitation Index (HALex), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Healthy Days questions, and self-rated health on a 5-category scale ranging from excellent to poor were plotted.
Results: SF-6D and QWB-SA are nearly linear across the range of but with a shallow slope; EQ-5D, HUI2, and HUI3 are linear with a steep slope from low (poor health) into midrange of , then approximately linear with a less steep slope for higher (health just below to well above average), although the inflection points differ by index.
Conclusion: Simple linear functions may serve as crosswalks among these indexes only for lower health states, albeit with low precision. Ceiling effects make crosswalks among most of the indexes ill specified above a certain level of health. Although each index measures generic health on a utility scale, these indexes are not identical but are relatively simply, if imprecisely, related.
Figures






References
-
- Houle C, Berthelot J-M. A Head-to-Head Comparison of the Health Utilities Index Mark 3 and the EQ-5D for the Population Living in Private Households in Canada. Quality of Life Newsletter. 2000;24:5–6. MAPI Institute.
-
- Kaplan RM, Groessl EJ, Sengupta N, et al. Comparison of measured utility scores and imputed scores from the SF-36 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med Care. 2005;43:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Luo N, Chew LH, Fong KY, et al. A comparison of the EuroQol-5D and the Health Utilities Index mark 3 in patients with rheumatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2268–74. - PubMed
-
- Luo N, Johnson JA, Shaw JW, et al. Self-Reported Health Status of the General Adult US Population as Assessed by the EQ-5D and Health Utilities Index. Med Care. 2005;43:1078–86. - PubMed
-
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Feeny DH. Responsiveness of generic health-related quality of life measures in stroke. Qual Life Res. 2005;14:207–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

