Molecular docking screens using comparative models of proteins
- PMID: 19845314
- PMCID: PMC2790034
- DOI: 10.1021/ci9003706
Molecular docking screens using comparative models of proteins
Abstract
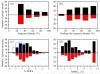
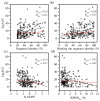
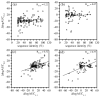
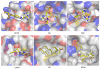
Two orders of magnitude more protein sequences can be modeled by comparative modeling than have been determined by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. Investigators have nevertheless been cautious about using comparative models for ligand discovery because of concerns about model errors. We suggest how to exploit comparative models for molecular screens, based on docking against a wide range of crystallographic structures and comparative models with known ligands. To account for the variation in the ligand-binding pocket as it binds different ligands, we calculate "consensus" enrichment by ranking each library compound by its best docking score against all available comparative models and/or modeling templates. For the majority of the targets, the consensus enrichment for multiple models was better than or comparable to that of the holo and apo X-ray structures. Even for single models, the models are significantly more enriching than the template structure if the template is paralogous and shares more than 25% sequence identity with the target.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Information decay in molecular docking screens against holo, apo, and modeled conformations of enzymes.J Med Chem. 2003 Jul 3;46(14):2895-907. doi: 10.1021/jm0300330. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12825931
-
Protein structure prediction provides comparable performance to crystallographic structures in docking-based virtual screening.Methods. 2015 Jan;71:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.08.017. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25220914 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the structure of opioid receptors with homology modeling based on single and multiple templates and subsequent docking: a comparative study.J Mol Model. 2011 May;17(5):1207-21. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0803-8. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Mol Model. 2011. PMID: 20661609
-
Comparative protein modeling by satisfaction of spatial restraints.Mol Med Today. 1995 Sep;1(6):270-7. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(95)91170-7. Mol Med Today. 1995. PMID: 9415161 Review.
-
Homology modeling of G-protein-coupled receptors with X-ray structures on the rise.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2010 May;13(3):317-25. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2010. PMID: 20443165 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel selective thiadiazine DYRK1A inhibitor lead scaffold with human pancreatic β-cell proliferation activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Sep 5;157:1005-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30170319 Free PMC article.
-
Compound Ranking Based on Fuzzy Three-Dimensional Similarity Improves the Performance of Docking into Homology Models of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors.ACS Omega. 2017 Jun 30;2(6):2583-2592. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00330. Epub 2017 Jun 8. ACS Omega. 2017. PMID: 30023670 Free PMC article.
-
Unmet challenges of structural genomics.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010 Oct;20(5):587-97. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.08.001. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20810277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated computational and Drosophila cancer model platform captures previously unappreciated chemicals perturbing a kinase network.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Apr 26;15(4):e1006878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006878. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31026276 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling lipid-protein interactions using nonquenched fluorescent liposomal nanovesicles and proteome microarrays.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Nov;11(11):1177-90. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.017426. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22843995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuntz ID. Structure-Based Strategies for Drug Design and Discovery. Science. 1992;257(5073):1078–1082. - PubMed
-
- Klebe G. Recent developments in structure-based drug design. J. Mol. Med. 2000;78(5):269–281. - PubMed
-
- Ealick SE, Armstrong SR. Pharmacologically relevant proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1993;3(6):861–867.
-
- Gschwend DA, Good AC, Kuntz ID. Molecular docking towards drug discovery. J. Mol. Recognit. 1996;9(2):175–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

