Validity of real time ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis: a prospective study
- PMID: 19846234
- PMCID: PMC6136148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.09.001
Validity of real time ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis: a prospective study
Abstract
Background/aims: Ultrasound is used to screen for hepatic steatosis, the most common liver disease in the United States. However, few studies have prospectively evaluated the accuracy of ultrasound to diagnose hepatic steatosis. Therefore, a double blinded prospective study was performed in consecutive patients undergoing liver biopsy to evaluate the accuracy of ultrasound to diagnose hepatic steatosis.
Methods: Real time ultrasound was performed just prior to the biopsy by a single investigator masked to the clinical diagnosis. The liver biopsy was reviewed by a pathologist masked to the clinical indication or sonographic findings.
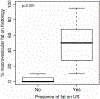
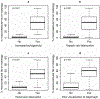
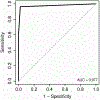
Results: Of 73 consecutive patients studied, macrovesicular steatosis of any severity on biopsy was found in 46 (63%) and micro vesicular fat found in 51 (69.9%). The overall impression of the sonographer for the presence of macrovesicular hepatic steatosis of any degree had a sensitivity of 60.9% and a specificity of 100%. The sensitivity increased to 100% and the specificity to 90% when there was > or =20% of fat. The zonular distribution of the fat did not alter the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound. Ultrasound had a poor yield in the diagnosis of microvesicular fat with an overall sensitivity of 43% and a specificity of 73%. The combination of increased echogenicity and portal vein blurring on ultrasound had the greatest sensitivity in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis.
Conclusion: Real time ultrasound using a combination of sonographic findings has a high specificity but underestimates the prevalence of hepatic steatosis when there is<20% fat.
Figures
References
-
- Tarantino G Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and other illnesses. Clin Invest Med 2008;31 :E290–E295. - PubMed
-
- Torres DM, Harrison SA. Diagnosis and therapy of nonalcoholic steatohepatities. Gastroenterology 2008; 134:1682–1698. - PubMed
-
- Perez NE, Siddiqui FA, Mutchnick MG, Dhar R, Tobi M, Ullah N, et al. Ultrasound diagnosis of fatty liver in patients with chronic liver disease: a retrospective observational study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007;41:624–629. - PubMed
-
- Strauss S, Gavish E, Gottlieb P, Katsnelson L. Interobserver and intraobserver variability in the sonographic assessment of fatty liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007; 189:W320–W323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

