Meta- and pooled analyses of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism and colorectal cancer: a HuGE-GSEC review
- PMID: 19846566
- PMCID: PMC2781761
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwp275
Meta- and pooled analyses of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism and colorectal cancer: a HuGE-GSEC review
Abstract
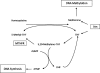
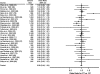
Worldwide, over 1 million cases of colorectal cancer (CRC) were reported in 2002, with a 50% mortality rate, making CRC the second most common cancer in adults. Certain racial/ethnic populations continue to experience a disproportionate burden of CRC. A common polymorphism in the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene has been associated with a lower risk of CRC. The authors performed both a meta-analysis (29 studies; 11,936 cases, 18,714 controls) and a pooled analysis (14 studies; 5,068 cases, 7,876 controls) of the C677T MTHFR polymorphism and CRC, with stratification by racial/ethnic population and behavioral risk factors. There were few studies on different racial/ethnic populations. The overall meta-analysis odds ratio for CRC for persons with the TT genotype was 0.83 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.77, 0.90). An inverse association was observed in whites (odds ratio = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74, 0.94) and Asians (odds ratio = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.67, 0.96) but not in Latinos or blacks. Similar results were observed for Asians, Latinos, and blacks in the pooled analysis. The inverse association between the MTHFR 677TT polymorphism and CRC was not significantly modified by smoking status or body mass index; however, it was present in regular alcohol users only. The MTHFR 677TT polymorphism seems to be associated with a reduced risk of CRC, but this may not hold true for all populations.
Figures

References
-
- Goyette P, Pai A, Milos R, et al. Gene structure of human and mouse methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) Mamm Genome. 1998;9(8):652–656. - PubMed
-
- Lucock M. Folic acid: nutritional biochemistry, molecular biology, and role in disease processes. Mol Genet Metab. 2000;71(1-2):121–138. - PubMed
-
- Stern LL, Mason JB, Selhub J, et al. Genomic DNA hypomethylation, a characteristic of most cancers, is present in peripheral leukocytes of individuals who are homozygous for the C677T polymorphism in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9(8):849–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

