The time course of dopamine transmission in the ventral tegmental area
- PMID: 19846722
- PMCID: PMC2791792
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3546-09.2009
The time course of dopamine transmission in the ventral tegmental area
Abstract
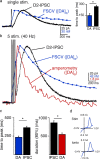
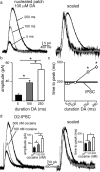
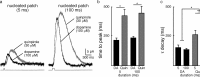
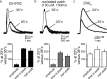
Synaptic transmission mediated by G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) is not generally thought to be point-to-point. To determine the extent over which dopamine signals in the midbrain, the present study examined the concentration and time course of dopamine that underlies a D(2)-receptor IPSC (D(2)-IPSC) in the ventral tegmental area. Extracellular dopamine was measured electrochemically while simultaneously recording D(2)-IPSCs. The presence of dopamine was brief relative to the IPSC, suggesting that G-protein dependent potassium channel activation determined the IPSC time course. The activation kinetics of D(2) receptor-dependent potassium current was studied using outside-out patch recordings with rapid application of dopamine. Dopamine applied at a minimum concentration of 10 mum for a maximum of 100 ms mimicked the IPSC. Higher concentrations applied for as little as 5 ms did not change the kinetics of the current. The results indicate that both the intrinsic kinetics of G-protein coupled receptor signaling and a rapidly rising high concentration of dopamine determine the time course of the IPSC. Thus, dopamine transmission in the midbrain is more localized then previously proposed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spontaneous inhibitory synaptic currents mediated by a G protein-coupled receptor.Neuron. 2013 Jun 5;78(5):807-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.013. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23764286 Free PMC article.
-
Control of extracellular dopamine at dendrite and axon terminals.J Neurosci. 2010 May 19;30(20):6975-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1020-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20484639 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo ethanol experience increases D(2) autoinhibition in the ventral tegmental area.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 Apr;36(5):993-1002. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.237. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21248720 Free PMC article.
-
Species differences in somatodendritic dopamine transmission determine D2-autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of ventral tegmental area neuron firing.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 26;32(39):13520-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2745-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23015441 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine inhibits GABA(A) currents in ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons via activation of presynaptic G-protein coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels.Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 17;165(4):1159-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.045. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19944748
Cited by
-
Spontaneous inhibitory synaptic currents mediated by a G protein-coupled receptor.Neuron. 2013 Jun 5;78(5):807-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.013. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23764286 Free PMC article.
-
Modified viral-genetic mapping reveals local and global connectivity relationships of ventral tegmental area dopamine cells.Elife. 2022 May 23;11:e76886. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76886. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35604019 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Heterogeneity of D2-Receptor Signaling in the Dorsal Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens.Neuron. 2018 May 2;98(3):575-587.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.038. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29656874 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine Release Dynamics in the Nucleus Accumbens Are Modulated by the Timing of Electrical Stimulation Pulses When Applied to the Medial Forebrain Bundle and Medial Prefrontal Cortex.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Jul 17;15(14):2643-2653. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00115. Epub 2024 Jul 3. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38958080 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal scales of dopamine transmission.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Jun;22(6):345-358. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00455-7. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33837376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barbour B, Keller BU, Llano I, Marty A. Prolonged presence of glutamate during excitatory synaptic transmission to cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994;12:1331–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bath BD, Michael DJ, Trafton BJ, Joseph JD, Runnels PL, Wightman RM. Subsecond adsorption and desorption of dopamine at carbon-fiber microelectrodes. Anal Chem. 2000;72:5994–6002. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead MJ, Grandy DK, Wickman K, Williams JT. Vesicular dopamine release elicits an inhibitory postsynaptic current in midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuron. 2004;42:939–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
