X-ray structure of Pur-alpha reveals a Whirly-like fold and an unusual nucleic-acid binding surface
- PMID: 19846792
- PMCID: PMC2765457
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907990106
X-ray structure of Pur-alpha reveals a Whirly-like fold and an unusual nucleic-acid binding surface
Abstract
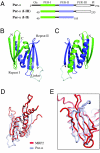
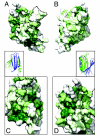
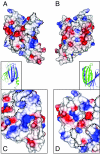
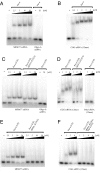
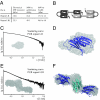
The PUR protein family is a distinct and highly conserved class that is characterized by its sequence-specific RNA- and DNA-binding. Its best-studied family member, Pur-alpha, acts as a transcriptional regulator, as host factor for viral replication, and as cofactor for mRNP localization in dendrites. Pur-alpha-deficient mice show severe neurologic defects and die after birth. Nucleic-acid binding by Pur-alpha is mediated by its central core region, for which no structural information is available. We determined the x-ray structure of residues 40 to 185 from Drosophila melanogaster Pur-alpha, which constitutes a major part of the core region. We found that this region contains two almost identical structural motifs, termed "PUR repeats," which interact with each other to form a PUR domain. DNA- and RNA-binding studies confirmed that PUR domains are indeed functional nucleic-acid binding domains. Database analysis show that PUR domains share a fold with the Whirly class of nucleic-acid binding proteins. Structural analysis combined with mutational studies suggest that a PUR domain binds nucleic acids through two independent surface regions involving concave beta-sheets. Structure-based sequence alignment revealed that the core region harbors a third PUR repeat at its C terminus. Subsequent characterization by small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) and size-exclusion chromatography indicated that PUR repeat III mediates dimerization of Pur-alpha. Surface envelopes calculated from SAXS data show that the Pur-alpha dimer consisting of repeats I to III is arranged in a Z-like shape. This unexpected domain organization of the entire core domain of Pur-alpha has direct implications for ssDNA/ssRNA and dsDNA binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kanai Y, Dohmae N, Hirokawa N. Kinesin transports RNA: Isolation and characterization of an RNA-transporting granule. Neuron. 2004;43:513–525. - PubMed
-
- Ohashi S, et al. Identification of mRNA/protein (mRNP) complexes containing Pur-alpha, mStaufen, fragile X protein, and myosin Va and their association with rough endoplasmic reticulum equipped with a kinesin motor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:37804–37810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

