Adipocyte turnover: relevance to human adipose tissue morphology
- PMID: 19846802
- PMCID: PMC2797910
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0942
Adipocyte turnover: relevance to human adipose tissue morphology
Abstract
Objective: Adipose tissue may contain few large adipocytes (hypertrophy) or many small adipocytes (hyperplasia). We investigated factors of putative importance for adipose tissue morphology.
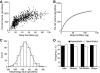
Research design and methods: Subcutaneous adipocyte size and total fat mass were compared in 764 subjects with BMI 18-60 kg/m(2). A morphology value was defined as the difference between the measured adipocyte volume and the expected volume given by a curved-line fit for a given body fat mass and was related to insulin values. In 35 subjects, in vivo adipocyte turnover was measured by exploiting incorporation of atmospheric (14)C into DNA.
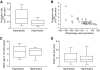
Results: Occurrence of hyperplasia (negative morphology value) or hypertrophy (positive morphology value) was independent of sex and body weight but correlated with fasting plasma insulin levels and insulin sensitivity, independent of adipocyte volume (beta-coefficient = 0.3, P < 0.0001). Total adipocyte number and morphology were negatively related (r = -0.66); i.e., the total adipocyte number was greatest in pronounced hyperplasia and smallest in pronounced hypertrophy. The absolute number of new adipocytes generated each year was 70% lower (P < 0.001) in hypertrophy than in hyperplasia, and individual values for adipocyte generation and morphology were strongly related (r = 0.7, P < 0.001). The relative death rate (approximately 10% per year) or mean age of adipocytes (approximately 10 years) was not correlated with morphology.
Conclusions: Adipose tissue morphology correlates with insulin measures and is linked to the total adipocyte number independently of sex and body fat level. Low generation rates of adipocytes associate with adipose tissue hypertrophy, whereas high generation rates associate with adipose hyperplasia.
Figures

References
-
- Wajchenberg BL: Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev 2000;21:697–738 - PubMed
-
- Bays HE, González-Campoy JM, Bray GA, Kitabchi AE, Bergman DA, Schorr AB, Rodbard HW, Henry RR: Pathogenic potential of adipose tissue and metabolic consequences of adipocyte hypertrophy and increased visceral adiposity. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2008;6:343–368 - PubMed
-
- Bjorntorp P, Sjostrom L: Number and size of adipose tissue fat cells in relation to metabolism in human obesity. Metabolism 1971;20:703–713 - PubMed
-
- Björntorp P, Bengtsson C, Blohmé G, Jonsson A, Sjöström L, Tibblin E, Tibblin G, Wilhelmsen L: Adipose tissue fat cell size and number in relation to metabolism in randomly selected middle-aged men and women. Metabolism 1971;20:927–935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

