Seven-month developmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants enrolled in a randomized controlled trial of delayed versus immediate cord clamping
- PMID: 19847185
- PMCID: PMC2799542
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2009.170
Seven-month developmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants enrolled in a randomized controlled trial of delayed versus immediate cord clamping
Abstract
Objective: The results from our previous trial revealed that infants with delayed cord clamping (DCC) had significantly lesser intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and late-onset sepsis (LOS) than infants with immediate cord clamping (ICC). A priori, we hypothesized that infants with DCC would have better motor function by 7 months corrected age.
Study design: Infants between 24 and 31 weeks were randomized to ICC or DCC and follow-up evaluation was completed at 7 months corrected age.
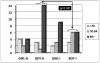
Result: We found no differences in the Bayley Scales of Infant Development (BSID) scores between the DCC and ICC groups. However, a regression model of effects of DCC on motor scores controlling for gestational age, IVH, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, sepsis and male gender suggested higher motor scores of male infants with DCC.
Conclusion: DCC at birth seems to be protective of very low birth weight male infants against motor disability at 7 months corrected age.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to report.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cord clamping and neurodevelopmental outcome in very low birth weight infants.J Perinatol. 2010 Jan;30(1):1. doi: 10.1038/jp.2009.177. J Perinatol. 2010. PMID: 20038938 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aladangady N, McHugh S, Aitchison TC, Wardrop CA, Holland BM. Infants’ blood volume in a controlled trial of placental transfusion at preterm delivery. Pediatrics. 2006;117(1):93–8. - PubMed
-
- Rabe H, Reynolds G, Diaz-Rossello J. Early versus delayed umbilical cord clamping in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(4):CD003248. - PubMed
-
- Rabe H, Reynolds G, Diaz-Rossello J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of a brief delay in clamping the umbilical cord of preterm infants. Neonatology. 2008;93(2):138–44. - PubMed
-
- Mercer J, McGrath M, Hensman A, Silver H, Oh W. Immediate and delayed cord clamping in infants born between 24 and 32 weeks: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Perinatol. 2003;23(6):466–72. - PubMed
-
- Nelle M, Fischer S, Conze S, Beedgen B, Brischke EM, Linderkamp O. Effects of later cord clamping on circulation in prematures (Abstract) Pediatr Res. 1998;44:420.

