An eight-gene blood expression profile predicts the response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19847310
- PMCID: PMC2762038
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007556
An eight-gene blood expression profile predicts the response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: TNF alpha blockade agents like infliximab are actually the treatment of choice for those rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who fail standard therapy. However, a considerable percentage of anti-TNF alpha treated patients do not show a significant clinical response. Given that new therapies for treatment of RA have been recently approved, there is a pressing need to find a system that reliably predicts treatment response. We hypothesized that the analysis of whole blood gene expression profiles of RA patients could be used to build a robust predictor to infliximab therapy.
Methods and findings: We performed microarray gene expression analysis on whole blood RNA samples from RA patients starting infliximab therapy (n = 44). The clinical response to infliximab was determined at week 14 using the EULAR criteria. Blood cell populations were determined using flow cytometry at baseline, week 2 and week 14 of treatment. Using complete cross-validation and repeated random sampling we identified a robust 8-gene predictor model (96.6% Leave One Out prediction accuracy, P = 0.0001). Applying this model to an independent validation set of RA patients, we estimated an 85.7% prediction accuracy (75-100%, 95% CI). In parallel, we also observed a significantly higher number of CD4+CD25+ cells (i.e. regulatory T cells) in the responder group compared to the non responder group at baseline (P = 0.0009).
Conclusions: The present 8-gene model obtained from whole blood expression efficiently predicts response to infliximab in RA patients. The application of the present system in the clinical setting could assist the clinician in the selection of the optimal treatment strategy in RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


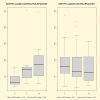
References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2007;370:1861–1874. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Julià A, Ballina J, Cañete J, Balsa A, Tornero-Molina J, et al. Genome-wide association study of rheumatoid arthritis in the Spanish population: KLF12 as a risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:2275–2286. - PubMed
-
- Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994;344:1105–1110. - PubMed
-
- Strand V, Kimberly R, Isaacs JD. Biologic therapies in rheumatology: lessons learned, future directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:75–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

