Design of a water coupling bolus with improved flow distribution for multi-element superficial hyperthermia applicators
- PMID: 19848618
- PMCID: PMC2783616
- DOI: 10.3109/02656730903124506
Design of a water coupling bolus with improved flow distribution for multi-element superficial hyperthermia applicators
Abstract
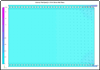
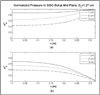
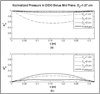
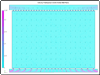
A water bolus used in superficial hyperthermia couples the electromagnetic (EM) or acoustic energy into the target tissue and cools the tissue surface to minimise thermal hotspots and patient discomfort during treatment. Parametric analyses of the fluid pressure inside the bolus computed using 3D fluid dynamics simulations are used in this study to determine a bolus design with improved flow and surface temperature distributions for large area superficial heat applicators. The simulation results are used in the design and fabrication of a 19 x 32 cm prototype bolus with dual input-dual output (DIDO) flow channels. Sequential thermal images of the bolus surface temperature recorded for a step change in the circulating water temperature are used to assess steady state flow and surface temperature distributions across the bolus. Modelling and measurement data indicate substantial improvement in bolus flow and surface temperature distributions when changing from the previous single input-single output (SISO) to DIDO configuration. Temperature variation across the bolus at steady state was measured to be less than 0.8 degrees C for the DIDO bolus compared to 1.5 degrees C for the SISO water bolus. The new DIDO bolus configuration maintains a nearly uniform flow distribution and low variation in surface temperature over a large area typically treated in superficial hyperthermia.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Quality assurance guidelines for superficial hyperthermia clinical trials : II. Technical requirements for heating devices.Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 May;193(5):351-366. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1106-0. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 28251250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow patterns and heat convection in a rectangular water bolus for use in superficial hyperthermia.Phys Med Biol. 2009 Jul 7;54(13):3937-53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/13/001. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Phys Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19494426 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal characteristics of thermobrachytherapy surface applicators for treating chest wall recurrence.Phys Med Biol. 2010 Apr 7;55(7):1949-69. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/7/011. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20224154 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a beam shaping bolus for superficial microwave hyperthermia waveguide applicators using a finite element method.Phys Med Biol. 2003 Jan 7;48(1):1-18. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/48/1/301. Phys Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12564497
-
Conformal microwave array (CMA) applicators for hyperthermia of diffuse chest wall recurrence.Int J Hyperthermia. 2010;26(7):686-98. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2010.501511. Int J Hyperthermia. 2010. PMID: 20849262 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quality assurance guidelines for superficial hyperthermia clinical trials : II. Technical requirements for heating devices.Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 May;193(5):351-366. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1106-0. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 28251250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow patterns and heat convection in a rectangular water bolus for use in superficial hyperthermia.Phys Med Biol. 2009 Jul 7;54(13):3937-53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/13/001. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Phys Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19494426 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical assessment of comfort and secure fit of thermobrachytherapy surface applicator (TBSA) on volunteer subjects.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012 Sep 6;13(5):3845. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v13i5.3845. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22955650 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal characteristics of thermobrachytherapy surface applicators for treating chest wall recurrence.Phys Med Biol. 2010 Apr 7;55(7):1949-69. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/7/011. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20224154 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation techniques in hyperthermia treatment planning.Int J Hyperthermia. 2013 Jun;29(4):346-57. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.790092. Epub 2013 May 14. Int J Hyperthermia. 2013. PMID: 23672453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones E, et al. Randomized trial of hyperthermia and radiation for superficial tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(13):3079–3085. - PubMed
-
- Kapp DS. Efficacy of adjuvant hyperthermia in the treatment of superficial recurrent breast cancer: confirmation and future directions. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology and Physics. 1996;35(5):1117–1121. - PubMed
-
- Sneed PK, et al. Survival benefit of hyperthermia in a prospective randomized trial of brachytherapy boost +/− hyperthermia for glioblastoma multiforme. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology and Physics. 1998;40(2):287–295. - PubMed
-
- Vernon CC, et al. Radiotherapy with or without hyperthermia in the treatment of superficial localized breast cancer: Results from five randomized controlled trials. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology and Physics. 1996;35(4):731–744. - PubMed
-
- Dewey WC, et al. In: Cell biology of hyperthermia and radiation, in Radiation Biology in Cancer Research. Meyn RE, Withers HR, editors. New York: Raven Press; 1980. pp. 589–621.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
