Astrocyte secreted proteins selectively increase hippocampal GABAergic axon length, branching, and synaptogenesis
- PMID: 19850128
- PMCID: PMC2818511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.10.004
Astrocyte secreted proteins selectively increase hippocampal GABAergic axon length, branching, and synaptogenesis
Abstract
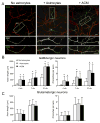
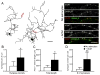
Astrocytes modulate the formation and function of glutamatergic synapses in the CNS, but whether astrocytes modulate GABAergic synaptogenesis is unknown. We demonstrate that media conditioned by astrocytes, but not other cells, enhanced GABAergic but not glutamatergic axon length and branching, and increased the number and density of presynaptically active GABAergic synapses in dissociated hippocampal cultures. Candidate mechanisms and factors, such as activity, neurotrophins, and cholesterol were excluded as mediating these effects. While thrombospondins secreted by astrocytes are necessary and sufficient to increase hippocampal glutamatergic synaptogenesis, they do not mediate astrocyte effects on GABAergic synaptogenesis. We show that the factors in astrocyte conditioned media that selectively affect GABAergic neurons are proteins. Taken together, our results show that astrocytes increase glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptogenesis via different mechanisms and release one or more proteins with the novel functions of increasing GABAergic axon length, branching and synaptogenesis.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Bloom FE. The formation of synaptic junctions in developing rat brain: a quantitative electron microscopic study. Brain Res. 1967;6:716–727. - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi A, Nishikawa K, Saito H, Abe K. Characterization of basic fibroblast growth factor-mediated acceleration of axonal branching in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1994;661:117–126. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Bergsman JB, Krueger SR, Fitzsimonds RM. Automated criteria-based selection and analysis of fluorescent synaptic puncta. J Neurosci Methods. 2006;152:32–39. - PubMed
-
- Cahoy JD, Emery B, Kaushal A, Foo LC, Zamanian JL, Christopherson KS, Xing Y, Lubischer JL, Krieg PA, Krupenko SA, Thompson WJ, Barres BA. A transcriptome database for astrocytes, neurons, and oligodendrocytes: a new resource for understanding brain development and function. J Neurosci. 2008;28:264–278. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

