Effects of human recombinant PEDF protein and PEDF-derived peptide 34-mer on choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 19850839
- PMCID: PMC2836227
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-4455
Effects of human recombinant PEDF protein and PEDF-derived peptide 34-mer on choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
Purpose: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a serpin with antiangiogenic properties. Previously, the authors showed that PEDF injected into the subconjunctiva reaches the choroid. Here, they examined the effects of PEDF polypeptide fragments on vessel sprouting and on choroidal neovascularization (CNV) after subconjunctival administration.
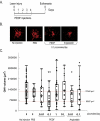
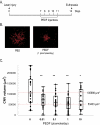
Methods: Recombinant human PEDF (rhuPEDF) was cleaved at its serpin-exposed loop by limited chymotrypsin proteolysis. Synthetic PEDF peptides 34-mer (Asp(44)-Asn(77)) and 44-mer (Val(78)-Thr(121)) were used. Ex vivo chick aortic vessel sprouting assays were performed. CNV was induced in rats by laser injury of Bruch's membrane. Daily subconjunctival injections (0.01-10 pmol/d protein) were performed for 5 days starting at day of injury or at the seventh day after injury. New vessel volumes were quantified using optical sections of choroid/RPE flat-mounts labeled with isolectin-Ib4. PEDF distribution was evaluated by immunofluorescence of choroid/RPE/retina cross-sections.
Results: Full-length rhuPEDF, cleaved rhuPEDF, or peptide 34-mer exhibited ex vivo antiangiogenic activity, but peptide 44-mer was inefficient. PEDF immunostaining around CNV lesions diminished after laser injury. Subconjunctival administration of rhuPEDF or 34-mer at 0.1 pmol/d decreased CNV lesion volumes by 52% and 47%, respectively, whereas those of 44-mer were similar to vehicle injections. Doses of 0.1 and 1 pmol/d rhuPEDF decreased fully developed CNV complex volumes by 45% and 50%, respectively, compared with vehicle injections.
Conclusions: A functional region for the inhibition of vessel sprouting and CNV resides within the 34-mer region of PEDF. Furthermore, subconjunctival administration of optimal range dosages of rhuPEDF or 34-mer can suppress and regress rat CNV lesions, demonstrating that these agents reach the choroid/RPE complex as functionally active molecules.
Figures

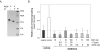
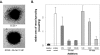

References
-
- Becerra SP. Focus on molecules: pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). Exp Eye Res 2006;82:739–740 - PubMed
-
- Filleur S, Nelius T, de Riese W, Kennedy RC. Characterization of PEDF: a multi-functional serpin family protein. J Cell Biochem 2009;106:769–775 - PubMed
-
- Amaral J, Becerra S. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor and Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer; 2008;311–337
-
- Bouck N. PEDF: anti-angiogenic guardian of ocular function. Trends Mol Med 2002;8:330–334 - PubMed
-
- Becerra SP. Structure-function studies on PEDF: a noninhibitory serpin with neurotrophic activity. Adv Exp Med Biol 1997;425:223–237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

