Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition
- PMID: 19850869
- PMCID: PMC2765921
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0905056106
Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition
Abstract
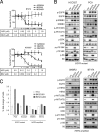
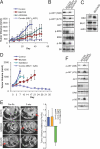
Non-small cell lung cancers with activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are highly responsive to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as gefitinib and erlotinib. Such cancers are "addicted" to EGFR, and treatment with a TKI invariably leads to down-regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR and MEK-ERK signaling pathways, resulting in apoptosis. Using a dual PI3K-mTOR inhibitor, NVP-BEZ235, we evaluated whether PI3K-mTOR inhibition alone induced apoptosis in these cancers. In contrast to HER2-amplified breast cancers, we found that PI3K-mTOR inhibition did not promote substantial apoptosis in the EGFR mutant lung cancers. However, blocking both PI3K-mTOR and MEK simultaneously led to apoptosis to similar levels as the EGFR TKIs, suggesting that down-regulation of these pathways may account for much of the apoptosis promoted by EGFR inhibition. In EGFR mutant lung cancers, down-regulation of both intracellular pathways converged on the BH3 family of proteins regulating apoptosis. PI3K inhibition led to down-regulation of Mcl-1, and MEK inhibition led to up-regulation of BIM. In fact, down-regulation of Mcl-1 by siRNA was sufficient to sensitize these cancers to single-agent MEK inhibitors. Surprisingly, an AKT inhibitor did not decrease Mcl-1 levels, and when combined with MEK inhibitors, failed to induce apoptosis. Importantly, we observed that the combination of PI3K-mTOR and MEK inhibitors effectively shrunk tumors in a transgenic and xenograft model of EGFR T790M-L858R cancers. These data indicate simultaneous inhibition of PI3K-mTOR and MEK signaling is an effective strategy for treating EGFR mutant lung cancers, including those with acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Sauveur-Michel Maira and Carlos Garcia-Echeverria are employees and stockholders of Novartis.
Figures
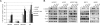

References
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Ulhoa-Cintra A, Greenberg L, Geyer CE. The emerging role of lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10:10–17. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Settleman J. Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer therapy. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Benvenuti S, et al. Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2643–2648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 AG024004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG2400401/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA137008-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120060-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08AG024004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

