Activation of nuclear receptor CAR ameliorates diabetes and fatty liver disease
- PMID: 19850873
- PMCID: PMC2773998
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909731106
Activation of nuclear receptor CAR ameliorates diabetes and fatty liver disease
Abstract
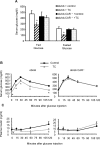
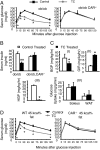
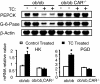
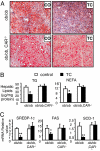
Constitutive androstane receptor CAR (NR1I3) has been identified as a central mediator of coordinate responses to xenobiotic and endobiotic stress. Here we use leptin-deficient mice (ob/ob) and ob/ob, CAR(-/-) double mutant mice to identify a metabolic role of CAR in type 2 diabetes. Activation of CAR significantly reduces serum glucose levels and improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Gene expression analyses and hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp results suggest that CAR activation ameliorates hyperglycemia by suppressing glucose production and stimulating glucose uptake and usage in the liver. In addition, CAR activation dramatically improves fatty liver by both inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis and induction of beta-oxidation. We conclude that CAR activation improves type 2 diabetes, and that these actions of CAR suggest therapeutic approaches to the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
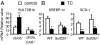
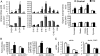
References
-
- Bouche C, Serdy S, Kahn CR, Goldfine AB. The cellular fate of glucose and its relevance in type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:807–830. - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD. Banting lecture 2001: Dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Accili D. Lilly lecture 2003: The struggle for mastery in insulin action: From triumvirate to republic. Diabetes. 2004;53:1633–1642. - PubMed
-
- Biddinger SB, Kahn CR. From mice to men: Insights into the insulin resistance syndromes. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:123–158. - PubMed
-
- Postic C, Dentin R, Girard J. Role of the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis. Diabetes Metab. 2004;30:398–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

