Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a SEIFEM-2008 registry study
- PMID: 19850903
- PMCID: PMC2857195
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.012054
Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a SEIFEM-2008 registry study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate prognostic factors, treatments and outcome of invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia based on data collected in a registry.
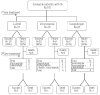
Design and methods: The registry, which was activated in 2004 and closed in 2007, collected data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia, admitted to 21 hematologic divisions in tertiary care centers or university hospitals in Italy, who developed proven or probable invasive aspergillosis.
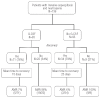
Results: One hundred and forty cases of invasive aspergillosis were collected, with most cases occurring during the period of post-induction aplasia, the highest risk phase in acute myeloid leukemia. The mortality rate attributable to invasive aspergillosis was 27%, confirming previous reports of a downward trend in this rate. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that the stage of acute myeloid leukemia and the duration of, and recovery from, neutropenia were independent prognostic factors. We analyzed outcomes after treatment with the three most frequently used drugs (liposomal amphotericin B, caspofungin, voriconazole). No differences emerged in survival at day 120 or in the overall response rate which was 71%, ranging from 61% with caspofungin to 84% with voriconazole.
Conclusions: Our series confirms the downward trend in mortality rates reported in previous series, with all new drugs providing similar survival and response rates. Recovery from neutropenia and disease stage are crucial prognostic factors. Efficacious antifungal drugs bridge the period of maximum risk due to poor hematologic and immunological reconstitution.
Figures
References
-
- Caira M, Girmenia C, Fadda RM, Mitra ME, Picardi M, Van Lint MT, et al. Invasive fungal infections in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and in those submitted to allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplant: who is at highest risk? Eur J Haematol. 2008;81(3):242–3. - PubMed
-
- Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, Offidani M, Fianchi L, Martino B, et al. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: the SEIFEM-2004 study. Haematologica. 2006;91(8):1068–75. - PubMed
-
- Herbrecht R, Natarajan-Amé S, Letscher-Bru V, Canuet M. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;25(2):191–202. - PubMed
-
- Baddley JW, Stroud TP, Salzman D, Pappas PG. Invasive mold infections in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(9):1319–24. - PubMed
-
- Klastersky J. Adverse effects of the humanized antibodies used as cancer therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18(4):316–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

