High-resolution structure of human carbonic anhydrase II complexed with acetazolamide reveals insights into inhibitor drug design
- PMID: 19851004
- PMCID: PMC2765883
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109036665
High-resolution structure of human carbonic anhydrase II complexed with acetazolamide reveals insights into inhibitor drug design
Abstract
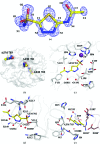
The crystal structure of human carbonic anhydrase II (CA II) complexed with the inhibitor acetazolamide (AZM) has been determined at 1.1 A resolution and refined to an R(cryst) of 11.2% and an R(free) of 14.7%. As observed in previous CA II-inhibitor complexes, AZM binds directly to the zinc and makes several key interactions with active-site residues. The high-resolution data also showed a glycerol molecule adjacent to the AZM in the active site and two additional AZMs that are adventitiously bound on the surface of the enzyme. The co-binding of AZM and glycerol in the active site demonstrate that given an appropriate ring orientation and substituents, an isozyme-specific CA inhibitor may be developed.
Figures
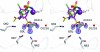
References
-
- Alterio, V., De Simone, G., Monti, S. M., Scozzafava, A. & Supuran, C. T. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.17, 4201–4207. - PubMed
-
- Berman, H., Henrick, K. & Nakamura, H. (2003). Nature Struct. Biol.10, 980. - PubMed
-
- Breinin, G. M. & Gortz, H. (1954). AMA Arch. Ophthalmol.52, 333–348. - PubMed
-
- DeLano, W. L. (2002). The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. http://www.pymol.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

