Perturbation-response scanning reveals ligand entry-exit mechanisms of ferric binding protein
- PMID: 19851447
- PMCID: PMC2758672
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000544
Perturbation-response scanning reveals ligand entry-exit mechanisms of ferric binding protein
Abstract
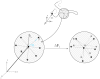
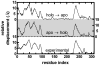
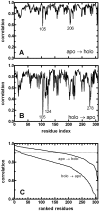
We study apo and holo forms of the bacterial ferric binding protein (FBP) which exhibits the so-called ferric transport dilemma: it uptakes iron from the host with remarkable affinity, yet releases it with ease in the cytoplasm for subsequent use. The observations fit the "conformational selection" model whereby the existence of a weakly populated, higher energy conformation that is stabilized in the presence of the ligand is proposed. We introduce a new tool that we term perturbation-response scanning (PRS) for the analysis of remote control strategies utilized. The approach relies on the systematic use of computational perturbation/response techniques based on linear response theory, by sequentially applying directed forces on single-residues along the chain and recording the resulting relative changes in the residue coordinates. We further obtain closed-form expressions for the magnitude and the directionality of the response. Using PRS, we study the ligand release mechanisms of FBP and support the findings by molecular dynamics simulations. We find that the residue-by-residue displacements between the apo and the holo forms, as determined from the X-ray structures, are faithfully reproduced by perturbations applied on the majority of the residues of the apo form. However, once the stabilizing ligand (Fe) is integrated to the system in holo FBP, perturbing only a few select residues successfully reproduces the experimental displacements. Thus, iron uptake by FBP is a favored process in the fluctuating environment of the protein, whereas iron release is controlled by mechanisms including chelation and allostery. The directional analysis that we implement in the PRS methodology implicates the latter mechanism by leading to a few distant, charged, and exposed loop residues. Upon perturbing these, irrespective of the direction of the operating forces, we find that the cap residues involved in iron release are made to operate coherently, facilitating release of the ion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang XJ, Wozniak JA, Matthews BW. Protein Flexibility and Adaptability Seen in 25 Crystal Forms of T4 Lysozyme. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1995;250:527–552. - PubMed
-
- Eisenmesser EZ, Millet O, Labeikovsky W, Korzhnev DM, Wolf-Watz M, et al. Intrinsic dynamics of an enzyme underlies catalysis. Nature. 2005;438:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Gunasekaran K, Ma BY, Nussinov R. Is allostery an intrinsic property of all dynamic proteins? Proteins-Structure Function and Bioinformatics. 2004;57:433–443. - PubMed
-
- Volkman BF, Lipson D, Wemmer DE, Kern D. Two-state allosteric behavior in a single-domain signaling protein. Science. 2001;291:2429–2433. - PubMed
-
- Tang C, Schwieters CD, Clore GM. Open-to-closed transition in apo maltose-binding protein observed by paramagnetic NMR. Nature. 2007;449:1078–1082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

