The TRAIL to targeted therapy of breast cancer
- PMID: 19854352
- PMCID: PMC3538140
- DOI: 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)03003-6
The TRAIL to targeted therapy of breast cancer
Abstract
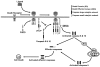
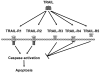
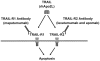
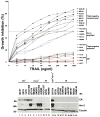
Breast cancers can be classified into those which express the estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PR) receptors, those with HER-2 amplification, and those without expression of ER, PR, or amplified HER-2 (referred to as triple-negative or basal-like breast cancer). Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) activates apoptosis upon binding to its receptors in many tumor types and the ligand and agonist antibodies are currently being studied in patients in clinical phases I and II trials. Cell line studies suggest that many breast cancer cell lines are very resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. However, recent data suggest that a subset of triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer cells is sensitive to TRAIL as a single agent. In addition, many studies have demonstrated that resistance to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells can be overcome by combinations of TRAIL with chemotherapy, radiation, and various targeted agents. This chapter will discuss the current understanding of the mechanisms, which control TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells. The preclinical data supporting the use of TRAIL ligands and agonistic antibodies alone and in combination in breast cancer will also be discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Aas T, Borresen AL, Geisler S, Smith-Sorensen B, Johnsen H, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA, Lonning PE. Specific P53 mutations are associated with de novo resistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. Nat Med. 1996;2:811–4. - PubMed
-
- Aktas O, Smorodchenko A, Brocke S, Infante-Duarte C, Schulze Topphoff U, Vogt J, Prozorovski T, Meier S, Osmanova V, Pohl E, Bechmann I, Nitsch R, Zipp F. Neuronal damage in autoimmune neuroinflammation mediated by the death ligand TRAIL. Neuron. 2005;46:421–32. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:420–30. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Holland P, Eckhardt SG. Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL) J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3621–30. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:155–162. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

