Deadenylation of maternal mRNAs mediated by miR-427 in Xenopus laevis embryos
- PMID: 19854872
- PMCID: PMC2779678
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1882009
Deadenylation of maternal mRNAs mediated by miR-427 in Xenopus laevis embryos
Abstract
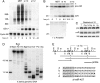
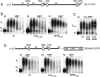
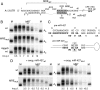
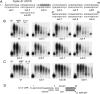
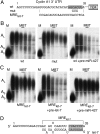
We show that microRNA-427 (miR-427) mediates the rapid deadenylation of maternal mRNAs after the midblastula transition (MBT) of Xenopus laevis embryogenesis. By MBT, the stage when the embryonic cell cycle is remodeled and zygotic transcription of mRNAs is initiated, each embryo has accumulated approximately 10(9) molecules of miR-427 processed from multimeric pri-miR-427 transcripts synthesized after fertilization. We demonstrate that the maternal mRNAs for cyclins A1 and B2 each contain a single miR-427 target sequence, spanning less than 30 nucleotides, that is both necessary and sufficient for deadenylation, and that inactivation of miR-427 leads to stabilization of the mRNAs. Although this deadenylation normally takes place after MBT, exogenous miRNAs produced prematurely in vivo can promote deadenylation prior to MBT, indicating that turnover of the maternal mRNAs is limited by the amount of accumulated miR-427. Injected transcripts comprised solely of the cyclin mRNA 3' untranslated regions or bearing a 5' ApppG cap undergo deadenylation, showing that translation of the targeted RNA is not required. miR-427 is not unique in promoting deadenylation, as an unrelated miRNA, let-7, can substitute for miR-427 if the reporter RNA contains an appropriate let-7 target site. We propose that miR-427, like the orthologous miR-430 of zebrafish, functions to down-regulate expression of maternal mRNAs early in development.
Figures


References
-
- Audic Y, Garbrecht M, Fritz B, Sheets MD, Hartley RS. Zygotic control of maternal cyclin A1 translation and mRNA stability. Dev Dyn. 2002;225:511–521. - PubMed
-
- Barnard DC, Ryan K, Manley JL, Richter JD. Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Ce1l. 2004;19:641–651. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
