The NCBI BioSystems database
- PMID: 19854944
- PMCID: PMC2808896
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp858
The NCBI BioSystems database
Abstract
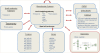
The NCBI BioSystems database, found at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/biosystems/, centralizes and cross-links existing biological systems databases, increasing their utility and target audience by integrating their pathways and systems into NCBI resources. This integration allows users of NCBI's Entrez databases to quickly categorize proteins, genes and small molecules by metabolic pathway, disease state or other BioSystem type, without requiring time-consuming inference of biological relationships from the literature or multiple experimental datasets.
Figures

References
-
- Klein TE, Chang JT, Cho MK, Easton KL, Fergerson R, Hewett M, Lin Z, Liu Y, Liu S, Oliver DE, et al. Integrating genotype and phenotype information: an overview of the PharmGKB project. Pharmacogenetics Research Network and Knowledge Base. Pharmacogenomics J. 2001;1:167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

