Allosteric control of catalysis by the F loop of RNA polymerase
- PMID: 19855007
- PMCID: PMC2776430
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0905402106
Allosteric control of catalysis by the F loop of RNA polymerase
Abstract
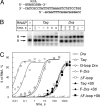
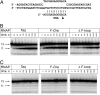
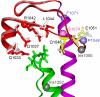
Bacterial RNA polymerases (RNAPs) undergo coordinated conformational changes during catalysis. In particular, concerted folding of the trigger loop and rearrangements of the bridge helix at the RNAP active center have been implicated in nucleotide addition and RNAP translocation. At moderate temperatures, the rate of catalysis by RNAP from thermophilic Thermus aquaticus is dramatically reduced compared with its closest mesophilic relative, Deinococcus radiodurans. Here, we show that a part of this difference is conferred by a third element, the F loop, which is adjacent to the N terminus of the bridge helix and directly contacts the folded trigger loop. Substitutions of amino acid residues in the F loop and in an adjacent segment of the bridge helix in T. aquaticus RNAP for their D. radiodurans counterparts significantly increased the rate of catalysis (up to 40-fold at 20 degrees C). A deletion in the F loop dramatically impaired the rate of nucleotide addition and pyrophosphorolysis, but it had only a moderate effect on intrinsic RNA cleavage. Streptolydigin, an antibiotic that blocks folding of the trigger loop, did not inhibit nucleotide addition by the mutant enzyme. The resistance to streptolydigin likely results from the loss of its functional target, the folding of the trigger loop, which is already impaired by the F-loop deletion. Our results demonstrate that the F loop is essential for proper folding of the trigger loop during nucleotide addition and governs the temperature adaptivity of RNAPs in different bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
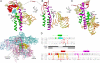

References
-
- Vassylyev DG, Vassylyeva MN, Perederina A, Tahirov TH, Artsimovitch I. Structural basis for transcription elongation by bacterial RNA polymerase. Nature. 2007;448:157–162. - PubMed
-
- Kettenberger H, Armache KJ, Cramer P. Complete RNA polymerase II elongation complex structure and its interactions with NTP and TFIIS. Mol Cell. 2004;16:955–965. - PubMed
-
- Vassylyev DG, et al. Structural basis for substrate loading in bacterial RNA polymerase. Nature. 2007;448:163–168. - PubMed
-
- Brueckner F, Cramer P. Structural basis of transcription inhibition by alpha-amanitin and implications for RNA polymerase II translocation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:811–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

