ATX-LPA receptor axis in inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 19855166
- PMCID: PMC4166520
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.22.9937
ATX-LPA receptor axis in inflammation and cancer
Abstract
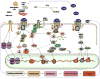
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA, 1- or 2-acyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) mediates a plethora of physiological and pathological activities via interactions with a series of high affinity G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). Both LPA receptor family members and autotaxin (ATX/LysoPLD), the primary LPA-producing enzyme, are aberrantly expressed in many human breast cancers and several other cancer lineages. Using transgenic mice expressing either an LPA receptor or ATX, we recently demonstrated that the ATX-LPA receptor axis plays a causal role in breast tumorigenesis and cancer-related inflammation, further validating the ATX-LPA receptor axis as a rich therapeutic target in cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Tokumura A. A family of phospholipid autacoids: occurrence, metabolism and bioactions. Prog Lipid Res. 1995;34:151–84. - PubMed
-
- An S, Bleu T, Hallmark OG, Goetzl EJ. Characterization of a novel subtype of human G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1998;273:7906–10. - PubMed
-
- Bandoh K, Hosono H, Kobayashi S, Kobayashi T, Murakami-Murofushi K, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human G-protein-coupled receptor, EDG7, for lysophosphatidic acid. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:27776–85. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi K, Ishii S, Shimizu T. Identification of p2y9/GPR23 as a novel G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid, structurally distant from the Edg family. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2003;278:25600–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
