Microduplications of 16p11.2 are associated with schizophrenia
- PMID: 19855392
- PMCID: PMC2951180
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.474
Microduplications of 16p11.2 are associated with schizophrenia
Abstract
Recurrent microdeletions and microduplications of a 600-kb genomic region of chromosome 16p11.2 have been implicated in childhood-onset developmental disorders. We report the association of 16p11.2 microduplications with schizophrenia in two large cohorts. The microduplication was detected in 12/1,906 (0.63%) cases and 1/3,971 (0.03%) controls (P = 1.2 x 10(-5), OR = 25.8) from the initial cohort, and in 9/2,645 (0.34%) cases and 1/2,420 (0.04%) controls (P = 0.022, OR = 8.3) of the replication cohort. The 16p11.2 microduplication was associated with a 14.5-fold increased risk of schizophrenia (95% CI (3.3, 62)) in the combined sample. A meta-analysis of datasets for multiple psychiatric disorders showed a significant association of the microduplication with schizophrenia (P = 4.8 x 10(-7)), bipolar disorder (P = 0.017) and autism (P = 1.9 x 10(-7)). In contrast, the reciprocal microdeletion was associated only with autism and developmental disorders (P = 2.3 x 10(-13)). Head circumference was larger in patients with the microdeletion than in patients with the microduplication (P = 0.0007).
Figures
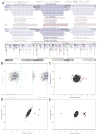
 ). MeZOD and the HMM algorithms detected the same deletions and duplications at 16p11.2.
). MeZOD and the HMM algorithms detected the same deletions and duplications at 16p11.2.References
-
- Weiss LA, et al. Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:667–75. - PubMed
-
- Kumar RA, et al. Recurrent 16p11.2 microdeletions in autism. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:628–38. - PubMed
-
- Walsh T, et al. Rare Structural Variants Disrupt Multiple Genes in Neurodevelopmental Pathways in Schizophrenia. Science. 2008;320:539–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DE016442/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- MH071523/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD04147/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000037/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HF004222/PHS HHS/United States
- MH083989/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH076431/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071523/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH081810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0800509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH031340/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01 MH090001/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH076431/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH081810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R41 DE016442/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH086756/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA MH002581/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MH061009/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH44245/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061009/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH31340/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH086756/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1U24MH081810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RR000037/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R42 DE016442/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- GM081519/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 HD004147/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083989/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH091350/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM081519/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

