miR-143 interferes with ERK5 signaling, and abrogates prostate cancer progression in mice
- PMID: 19855844
- PMCID: PMC2763222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007542
miR-143 interferes with ERK5 signaling, and abrogates prostate cancer progression in mice
Abstract
Background: Micro RNAs are small, non-coding, single-stranded RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Since miR-143 was found to be down-regulated in prostate cancer cells, we wanted to analyze its expression in human prostate cancer, and test the ability of miR-43 to arrest prostate cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
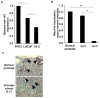
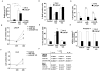
Results: Expression of miR-143 was analyzed in human prostate cancers by quantitative PCR, and by in situ hybridization. miR-143 was introduced in cancer cells in vivo by electroporation. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase-based assays were used to determine miR-143 targets. We show in this study that miR-143 levels are inversely correlated with advanced stages of prostate cancer. Rescue of miR-143 expression in cancer cells results in the arrest of cell proliferation and the abrogation of tumor growth in mice. Furthermore, we show that the effects of miR-143 are mediated, at least in part by the inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-5 (ERK5) activity. We show here that ERK5 is a miR-143 target in prostate cancer.
Conclusions: miR-143 is as a new target for prostate cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

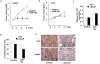
References
-
- Huggins C. Endocrine-induced regression of cancers. Science. 1967;156:1050–1054. - PubMed
-
- Feldman BJ, Feldman D. The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:34–45. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005;433:769–773. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T, Kissler S, et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature. 2008;456:980–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

