Open reduction and internal fixation compared to closed reduction and external fixation in distal radial fractures: a randomized study of 50 patients
- PMID: 19857180
- PMCID: PMC2823185
- DOI: 10.3109/17453670903171875
Open reduction and internal fixation compared to closed reduction and external fixation in distal radial fractures: a randomized study of 50 patients
Abstract
Background and purpose: In unstable distal radial fractures that are impossible to reduce or to maintain in reduced position, the treatment of choice is operation. The type of operation and the choice of implant, however, is a matter of discussion. Our aim was to investigate whether open reduction and internal fixation would produce a better result than traditional external fixation.
Methods: 50 patients with an unstable or comminute distal radius fracture were randomized to either closed reduction and bridging external fixation, or open reduction and internal fixation using the TriMed system. The primary outcome parameter was grip strength, but the patients were followed for 1 year with objective clinical assessment, subjective outcome using DASH, and radiographic examination.
Results: At 1 year postoperatively, grip strength was 90% (SD 16) of the uninjured side in the internal fixation group and 78% (17) in the external fixation group. Pronation/supination was 150 degrees (15) in the internal fixation group and 136 degrees (20) in the external fixation group at 1 year. There were no differences in DASH scores or in radiographic parameters. 5 patients in the external fixation group were reoperated due to malunion, as compared to 1 in the internal fixation group. 7 other cases were classified as radiographic malunion: 5 in the external fixation group and 2 in the internal fixation group.
Interpretation: Internal fixation gave better grip strength and a better range of motion at 1 year, and tended to have less malunions than external fixation. No difference could be found regarding subjective outcome.
Figures
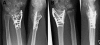
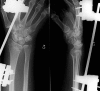

References
-
- Abramo A, Kopylov P, Tägil M. Evaluation of a treatment protocol in distal radius fractures. A prospective study in 581 patients using DASH as outcome. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(3):376–85. - PubMed
-
- Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Andersson B, Dahlgren E, Johansson A. The disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) outcome questionnaire: reliability and validity of the Swedish version evaluated in 176 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(6):613–8. - PubMed
-
- Atroshi I, Brogren E, Larsson GU, Kloow J, Hofer M, Berggren AM. Wrist-bridging versus non-bridging external fixation for displaced distal radius fractures: a randomized assessor-blind clinical trial of 38 patients followed for 1 year. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(3):445–53. - PubMed
-
- Benson LS, Minihane KP, Stern LD, Eller E, Seshadri R. The outcome of intra-articular distal radius fractures treated with fragment-specific fixation. J Hand Surg (Am) 2006;31(8):1333–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
