Prognostic and pathogenetic value of combining clinical and biochemical indices in patients with acute lung injury
- PMID: 19858233
- PMCID: PMC2816641
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.09-1484
Prognostic and pathogenetic value of combining clinical and biochemical indices in patients with acute lung injury
Abstract
Background: No single clinical or biologic marker reliably predicts clinical outcomes in acute lung injury (ALI)/ARDS. We hypothesized that a combination of biologic and clinical markers would be superior to either biomarkers or clinical factors alone in predicting ALI/ARDS mortality and would provide insight into the pathogenesis of clinical ALI/ARDS.
Methods: Eight biologic markers that reflect endothelial and epithelial injury, inflammation, and coagulation (von Willebrand factor antigen, surfactant protein D [SP-D]), tumor necrosis factor receptor-1, interleukin [IL]-6, IL-8, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, protein C, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) were measured in baseline plasma from 549 patients in the ARDSNet trial of low vs high positive end-expiratory pressure. Mortality was modeled with multivariable logistic regression. Predictors were selected using backward elimination. Comparisons between candidate models were based on the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) and tests of integrated discrimination improvement.
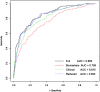
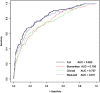
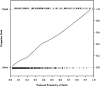
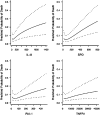
Results: Clinical predictors (Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation III [APACHE III], organ failures, age, underlying cause, alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient, plateau pressure) predicted mortality with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.82; a combination of eight biomarkers and the clinical predictors had an AUC of 0.85. The best performing biomarkers were the neutrophil chemotactic factor, IL-8, and SP-D, a product of alveolar type 2 cells, supporting the concept that acute inflammation and alveolar epithelial injury are important pathogenetic pathways in human ALI/ARDS.
Conclusions: A combination of biomarkers and clinical predictors is superior to clinical predictors or biomarkers alone for predicting mortality in ALI/ARDS and may be useful for stratifying patients in clinical trials. From a pathogenesis perspective, the degree of acute inflammation and alveolar epithelial injury are highly associated with the outcome of human ALI/ARDS.
Figures
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(18):1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Ware JH. The limitations of risk factors as prognostic tools. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(25):2615–2617. - PubMed
-
- Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, et al. NHLBI Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trials Network Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, et al. Significance of von Willebrand factor in septic and non-septic patients with acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(7):766–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 HL074005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL73996/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL074024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR046059/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL051856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HR46059/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL74024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL073994/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL73994/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL081332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL74005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL81332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL103836/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL073996/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

