An albumin-conjugated peptide exhibits potent anti-HIV activity and long in vivo half-life
- PMID: 19858258
- PMCID: PMC2798538
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00976-09
An albumin-conjugated peptide exhibits potent anti-HIV activity and long in vivo half-life
Erratum in
- Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Aug;54(8):3535
Abstract
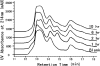
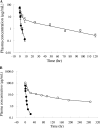
The clinical application of conventional peptide drugs often is limited by their short in vivo half-life and potential immunogenicity. Frequent injection presents challenges to the treatment of chronic diseases, such as HIV infection. We chemically modified a peptide HIV fusion inhibitor with 3-maleimidopropionic acid (MPA), which allows rapid and irreversible conjugation with serum albumin at a 1:1 molar ratio. FB006M, with an MPA modification at the 13th amino acid, rapidly formed conjugate with albumin upon intravenous injection, and it exhibited a remarkably extended in vivo half-life. The albumin conjugate of FB006M displayed potent inhibitory activity against a number of laboratory and clinical isolates of HIV-1 in vitro and in vivo. No immunogenicity or antibody formation was detected after repeated dosing. The clinical application of FB006M may decrease the cost of treatment and improve treatment compliance and patient quality of life.
Figures
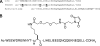
References
-
- Abu Ajaj, K., R. Graeser, I. Fichtner, and F. Kratz. 2009. In vitro and in vivo study of an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin that is cleaved by cathepsin B. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 64:413-418. - PubMed
-
- Balan, V., D. R. Nelson, M. S. Sulkowski, G. T. Everson, L. R. Lambiase, R. H. Wiesner, R. C. Dickson, A. B. Post, R. R. Redfield, G. L. Davis, A. U. Neumann, B. L. Osborn, W. W. Freimuth, and G. M. Subramanian. 2006. A phase I/II study evaluating escalating doses of recombinant human albumin-interferon-alpha fusion protein in chronic hepatitis C patients who have failed previous interferon-alpha-based therapy. Antivir. Ther. 11:35-45. - PubMed
-
- Buckheit, R. W., Jr., J. L. Roberson, C. Lackman-Smith, J. R. Wyatt, T. A. Vickers, and D. J. Ecker. 1994. Potent and specific inhibition of HIV envelope-mediated cell fusion and virus binding by G quartet-forming oligonucleotide (ISIS 5320). AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 10:1497-1506. - PubMed
-
- Buckheit, R. W., Jr., and R. Swanstrom. 1991. Characterization of an HIV-1 isolate displaying an apparent absence of virion-associated reverse transcriptase activity. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 7:295-302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

